(iii) cheese. (4 marks)
题目
(iii) cheese. (4 marks)
相似考题
更多“(iii) cheese. (4 marks)”相关问题
-
第1题:
(iii) job enrichment. (5 marks)
正确答案:
(iii) Job enrichment, which is often referred to as ‘vertical job enlargement’, is a planned, deliberate action to build greater responsibility, breadth and challenge into the work of the individual. The emphasis is on the individual rather than the organisation, team or group. This may be a way forward for some of Bailey’s employees since it provides the individual employee with the responsibility for decision making of a higher order, provides greater freedom to decide how the job or task should be undertaken, improves understanding of the entire process, encourages participation in the planning and production procedures and provides regular feedback to management – urgently needed at Bailey’s.
-
第2题:
4 (a) Explain the meaning of the term ‘working capital cycle’ for a trading company. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(a) The working capital cycle illustrates the changing make-up of working capital in the course of the trading operations of a
business:
1 Purchases are made on credit and the goods go into inventory.
2 Inventory is sold and converted into receivables
3 Credit customers pay their accounts
4 Cash is used to pay suppliers. -
第3题:
(iii) A statement on the importance of confidentiality in the financing of the early stage working capital needs
and an explanation of how this conflicts with the duty of transparency in matters of corporate
governance. (6 marks)
Professional marks for layout, logical flow and persuasiveness of the statement. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(iii) Importance of confidentiality in the financing of the project and the normal duty of transparency.
I have been asked to include a statement in my remarks on the balance between our duty to be transparent whenever
possible and the need for discretion and confidentiality in some situations. In the case of our initial working capital needs
for the Giant Dam Project, the importance of confidentiality in financing is due to the potential for adverse publicity that
may arise for the lender. It is important that R&M have the project adequately financed, especially in the early stages
before the interim payments from the client become fully effective.
In general, of course, we at R&M attempt to observe the highest standards of corporate governance and this involves
adopting a default position of transparency rather than concealment wherever possible. We recognise that transparency
is important to underpin investor confidence and to provide investors with the information they need to make fund
allocation decisions.
Whilst it is normal to disclose the amount of debt we carry at any given point (on the balance sheet), it is rarely normal
practice to disclose the exact sources of those loans. In the case of the financing of initial working capital for the Giant
Dam Project, I’m sure you will realise that in this unique situation, disclosure of the lender’s identity could threaten the
progress of the project. For this reason we must resist any attempts to release this into the public domain. We are aware
of one pressure group that is actively seeking to discover this information in order to disrupt the project’s progress and
we shall be taking all internal measures necessary to ensure they do not obtain the information.
Thank you for listening. -
第4题:
(iii) whether you agree or not with the statement of the production director. (3 marks)
正确答案:
(iii) ‘If we implement a reward scheme then it is bound to be beneficial for BGL’.
The statement of the manufacturing director is not necessarily correct. Indeed there is much evidence to support the
proposition that the existence of performance-related reward schemes can encourage dysfunctional behaviour. This often
manifests itself in the form. of ‘budgetary slack’ which is incorporated into budgets in anticipation of subsequent cuts by
higher levels of management or to make subsequent performance look better. -
第5题:
(iii) assesses TSC in terms of financial performance, competitiveness, service quality, resource utilisation,
flexibility and innovation and discusses the interrelationships between these terms, incorporating
examples from within TSC; and (10 marks)
正确答案:
(iii) The terms listed may be seen as representative of the dimensions of performance. The dimensions may be analysed into
results and determinants.
The results may be measured by focusing on financial performance and competitiveness. Financial performance may
be measured in terms of revenue and profit as shown in the data in the appendix of the question in respect of TSC. The
points system in part (a) of the answer shows which depots have achieved or exceeded the target set. In addition,
liquidity is another aspect of the measurement of financial performance. The points total in part (a) showed that
Leonardotown and Michaelangelotown depots appear to have the best current record in aspects of credit control.
15
Competitiveness may be measured in terms of sales growth but also in terms of market share, number of new
customers, etc. In the TSC statistics available in (a) we only have data for the current quarter. This shows that three of
the four depots listed have achieved increased revenue compared to target.
The determinants are the factors which may be seen to contribute to the achievement of the results. Quality, resource
utilisation, flexibility and innovation are cited by Fitzgerald and Moon as examples of factors that should contribute to
the achievement of the results in terms of financial performance and competitiveness. In TSC a main quality issue
appears to be customer care and service delivery. The statistics in the points table in part (a) of the answer show that
the Raphaeltown depot appears to have a major problem in this area. It has only achieved one point out of the six
available in this particular segment of the statistics.
Resource utilisation for TSC may be measured by the level of effective use of drivers and vehicles. To some extent, this
is highlighted by the statistics relating to customer care and service delivery. For example, late collection of consignments
from customers may be caused by a shortage of vehicles and/or drivers. Such shortages could be due to staff turnover,
sickness, etc or problems with vehicle maintenance.
Flexibility may be an issue. There may, for example, be a problem with vehicle availability. Possibly an increased focus
on sources for short-term sub-contracting of vehicles/collections/deliveries might help overcome delay problems.
The ‘target v actual points system’ may be seen as an example of innovation by the company. This gives a detailed set
of measures that should provide an incentive for improvement at all depots. The points system may illustrate the extent
of achievement/non-achievement of company strategies for success. For example TSC may have a customer care
commitment policy which identifies factors that should be achieved on a continuing basis. For example, timely collection
of consignments, misdirected consignments re-delivered at no extra charge, prompt responses to customer claims and
compensation for customers. -
第6题:
(iii) Identify and discuss an alternative strategy that may assist in improving the performance of CTC with
effect from 1 May 2009 (where only the products in (a) and (b) above are available for manufacture).
(4 marks)
正确答案:
(iii) If no new products are available then CTC must look to boost revenues obtained from its existing product portolio whilst
seeking to reduce product specific fixed overheads and the company’s other fixed overheads. In order to do this attention
should be focused on the marketing activities currently undertaken.
CTC should consider selling all of its products in ‘multi product’ packages as it might well be the case that the increased
contribution achieved from increased sales volumes would outweigh the diminution in contribution arising from
reductions in the selling price per unit of each product.
CTC could also apply target costing principles in order to reduce costs and thereby increase the margins on each of its
products. Value analysis should be undertaken in order to evaluate the value-added features of each product. For
example, the use of non-combustible materials in manufacture would be a valued added feature of such products
whereas the use of pins and metal fastenings which are potentially harmful to children would obviously not comprise
value added features. CTC should focus on delivering ‘value’ to the customer and in attempting to do so should seek to
identify all non-value activities in order that they may be eliminated and hence margins improved. -
第7题:
(iii) State the value added tax (VAT) and stamp duty (SD) issues arising as a result of inserting Bold plc as
a holding company and identify any planning actions that can be taken to defer or minimise these tax
costs. (4 marks)
You should assume that the corporation tax rates for the financial year 2005 and the income tax rates
and allowances for the tax year 2005/06 apply throughout this question.
正确答案:
(iii) Bold plc will be making a taxable supply of services, likely to exceed the VAT threshold. It should therefore consider
registering for VAT – either immediately on a voluntary basis, or when its cumulative taxable supplies in the previous
twelve months exceed £60,000.
As an alternative, the new group can apply for a group VAT registration. This will simplify its VAT administration as intragroup
transactions are broadly disregarded for VAT purposes, and only one VAT return is required for the group as a
whole.
Stamp duty normally applies at 0·5% on the consideration payable in respect of transactions in shares. However, an
exemption is available in the case of a takeover, reconstruction or amalgamation where there is no real change in
ownership, i.e. the new shareholdings mirror the old shareholdings, and the transaction is for commercial purposes. The
insertion of a new holding company over an existing company, as proposed here, would qualify for this exemption.
There is no VAT on transactions in shares. -
第8题:
(iii) Explain the potential corporation tax (CT) implications of Tay Limited transferring work to Trent Limited,
and suggest how these can be minimised or eliminated. (3 marks)
正确答案:
(iii) Trading losses may not be carried forward where, within a period of three years there is both a change in the ownership
of a company and a major change in the nature or conduct of its trade. The transfer of work from Tay Limited to Trent
Limited is likely to constitute a major change in the nature or conduct of the latter’s trade. As a consequence, any tax
losses at the date of acquisition will be forfeited. Assuming losses were incurred uniformly in 2005, the tax losses at the
date of acquisition were £380,000 (300,000 + 2/3 x 120,000)). This is worth £114,000 assuming a corporation tax
rate of 30%.
Thus, Tay Limited should not consider transferring any trade to Trent Limited until after the third anniversary of the date
of the change of ownership i.e. not before 1 September 2008. As the trades are similar, there should be little problem
in transferring work from that date onwards. -
第9题:
(c) Illustrate how:
(i) inquiry; and (4 marks)
正确答案:
(c) Due diligence review
(i) Inquiries
Tutorial note: These should be focussed on uncovering facts that may not be revealed by the audited financial
statements (e.g. off balance sheet finance, contingencies, commitments and contracts) especially where knowledge
may be confined to management.
■ Do any members of MCM’s senior/executive management have contractual terms that will result in significant
payouts to them (e.g. on change of ownership of the company or their being made redundant)?
■ What contracts with clients, if any, will lapse or be made void in the event that MCM is purchased from Frontiers?
■ What synergy or inter-company trading, if any, currently exists between MCM and Frontiers? For example, Frontiers
may publish MCM’s training materials.
■ Are there any major clients who are likely to be lost if MCM is purchased by Plaza (e.g. any competitor food
retailers)?
■ What are the principal terms of the operating leases relating to the International business’s premises?
■ What penalties should be expected to be incurred if operating leases and/or contracts with training consultants are
terminated?
■ Has MCM entered into any purchase commitments since 31 December 2004 (e.g. to buy or lease further
premises)?
■ Who are the best trainers that Plaza should seek to retain after the purchase of MCM?
■ What events since the audited financial statements to 31 December 2004 were published have made a significant
impact on MCM’s assets, liabilities, operating capability and/or cash flows? (For example, storm damage to
premises, major clients defaulting on payments, significant interest/foreign-exchange rate fluctuations, etc.)
■ Are there any unresolved tax issues which have not been provided for in full?
■ What effect will the purchase have on loan covenants? For example, term loans may be rendered repayable on a
change of ownership. -
第10题:
(iii) Can audit teams cross sell services to their clients? (4 marks)
Required:
For EACH of the three FAQs, explain the threats to objectivity that may arise and the safeguards that should
be available to manage them to an acceptable level.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three questions.
正确答案:
(iii) Cross selling services
The practice of cross selling is intended to give incentives to members of audit teams to concentrate their efforts on the
selling of non-audit services to audit clients.
It is not inappropriate for an audit firm to cross sell or for members of the audit team to recognise on an ongoing basis
the need of a client to have non audit services. However it should not be an aim of the audit team member to seek out
such opportunities.
Boleyn should have policies and procedures to ensure that, in relation to each audit client:
■ the objectives of the members of the audit team do not include selling of non-audit services to the audit client;
■ the criteria for evaluating the performance of members of the audit team do not include success in selling nonaudit
services to the audit client;
■ no specific element of remuneration of a member of the audit team and no decision concerning promotion within
the audit firm is based on his or her success in selling non-audit services to the audit client; and
■ the ethics partner being available for consultation when needed.
Therefore objectives such as the following are inappropriate:
■ to meet a quota of opportunities;
■ to specifically make time to discuss with clients which non-audit services they should consider;
■ to develop identified selling opportunities.
An audit engagement partner’s performance should be judged on the quality and integrity of the audit only. There are
no restrictions on normal partnership profit-sharing arrangements.
-
第11题:
(ii) Deema Co. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Deema Co
The claim is an event after the balance sheet date. If the accident occurred prior to the year end of 30 September 2007,
the claim gives additional evidence of a year end condition, and thus meets the definition of an adjusting post balance
sheet event. In this case the matter appears to have been properly disclosed in the notes to the financial statements per
IAS 10 Events After the Balance Sheet Date and IAS 37 Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets. A
provision would only be necessary if the claim was probable to succeed and there is sufficient appropriate evidence that
this is not the case. There is therefore no disagreement, and no limitation on scope.
Therefore the senior is correct to propose an unqualified opinion.
However, it is not necessary for the audit report to contain an emphasis of matter paragraph.
ISA 701 Modifications to the Independent Auditor’s Report states that an emphasis of matter paragraph should be used
to highlight a matter where there is significant uncertainty.
Uncertainties are normally only regarded as significant if they involve a level of concern about the going concern status
of the company or would have an unusually great effect on the financial statements. This is not the case here as there
is enough cash to pay the damages in the unlikely event that the claim goes against Deema Co. This appears to be a
one-off situation with a low risk of the estimate being subject to change and thus there is no significant uncertainty. -
第12题:
(a) List and explain FOUR methods of selecting a sample of items to test from a population in accordance with ISA 530 (Redrafted) Audit Sampling and Other Means of Testing. (4 marks)
(b) List and explain FOUR assertions from ISA 500 Audit Evidence that relate to the recording of classes of
transactions. (4 marks)
(c) In terms of audit reports, explain the term ‘modified’. (2 marks)
正确答案:
(a)SamplingmethodsMethodsofsamplinginaccordancewithISA530AuditSamplingandOtherMeansofTesting:Randomselection.Ensureseachiteminapopulationhasanequalchanceofselection,forexamplebyusingrandomnumbertables.Systematicselection.Inwhichanumberofsamplingunitsinthepopulationisdividedbythesamplesizetogiveasamplinginterval.Haphazardselection.Theauditorselectsthesamplewithoutfollowingastructuredtechnique–theauditorwouldavoidanyconsciousbiasorpredictability.Sequenceorblock.Involvesselectingablock(s)ofcontinguousitemsfromwithinapopulation.Tutorialnote:Othermethodsofsamplingareasfollows:MonetaryUnitSampling.Thisselectionmethodensuresthateachindividual$1inthepopulationhasanequalchanceofbeingselected.Judgementalsampling.Selectingitemsbasedontheskillandjudgementoftheauditor.(b)Assertions–classesoftransactionsOccurrence.Thetransactionsandeventsthathavebeenrecordedhaveactuallyoccurredandpertaintotheentity.Completeness.Alltransactionsandeventsthatshouldhavebeenrecordedhavebeenrecorded.Accuracy.Theamountsandotherdatarelatingtorecordedtransactionsandeventshavebeenrecordedappropriately.Cut-off.Transactionsandeventshavebeenrecordedinthecorrectaccountingperiod.Classification.Transactionsandeventshavebeenrecordedintheproperaccounts.(c)AuditreporttermModified.Anauditormodifiesanauditreportinanysituationwhereitisinappropriatetoprovideanunmodifiedreport.Forexample,theauditormayprovideadditionalinformationinanemphasisofmatter(whichdoesnotaffecttheauditor’sopinion)orqualifytheauditreportforlimitationofscopeordisagreement. -
第13题:
(iii) How items not dealt with by an IFRS for SMEs should be treated. (5 marks)
正确答案:
(iii) The treatment of items not dealt with by an IFRS for SMEs
IFRSs for SMEs would not necessarily deal with all the recognition and measurement issues facing an entity but the key
issues should revolve around the nature of the recognition, measurement and disclosure of the transactions of SMEs. In
the case where the item is not dealt with by the standards there are three alternatives:
(a) the entity can look to the full IFRS to resolve the issue
(b) management’s judgement can be used with reference to the Framework and consistency with other IFRSs for SMEs
(c) existing practice could be used.
The first approach is more likely to result in greater consistency and comparability. However, this approach may also
increase the burden on SMEs as it can be argued that they are subject to two sets of standards.
An SME may wish to make a disclosure required by a full IFRS which is not required by the SME standard, or a
measurement principle is simplified or exempted in the SME standard, or the IFRS may give a choice between two
measurement options and the SME standard does not allow choice. Thus the issue arises as to whether SMEs should
be able to choose to comply with a full IFRS for some items and SME standards for other items, allowing an SME to
revert to IFRS on a principle by principle basis. The problem which will arise will be a lack of consistency and
comparability of SME financial statements.
-
第14题:
(c) Mr Cobar, the chief executive of SHC, has decided to draft two alternative statements to explain both possible
outcomes of the secrecy/licensing decision to shareholders. Once the board has decided which one to pursue,
the relevant draft will be included in a voluntary section of the next corporate annual report.
Required:
(i) Draft a statement in the event that the board chooses the secrecy option. It should make a convincing
business case and put forward ethical arguments for the secrecy option. The ethical arguments should
be made from the stockholder (or pristine capitalist) perspective. (8 marks)
(ii) Draft a statement in the event that the board chooses the licensing option. It should make a convincing
business case and put forward ethical arguments for the licensing option. The ethical arguments should
be made from the wider stakeholder perspective. (8 marks)
(iii) Professional marks for the persuasiveness and logical flow of arguments: two marks per statement.
(4 marks)
正确答案:(c) (i) For the secrecy option
Important developments at SHC
This is an exciting time for the management and shareholders of Swan Hill Company. The research and development
staff at SHC have made a groundbreaking discovery (called the ‘sink method’) that will enable your company to produce
its major product at lower cost, in higher volumes and at a much higher quality than our competitors will be able to
using, as they do, the existing production technology. The sink process also produces at a lower rate of environmental
emissions which, as I’m sure shareholders will agree, is a very welcome development.
When considering the options following the discovery, your board decided that we should press ahead with the
investment needed to transform. the production facilities without offering the use of the technology to competitors under
a licensing arrangement. This means that once the new sink production comes on stream, SHC shareholders can, your
board believes, look forward to a significant strengthening of our competitive position.
The business case for this option is overwhelming. By pushing ahead with the investment needed to implement the sink
method, the possibility exists to gain a substantial competitive advantage over all of SHC’s competitors. It will place SHC
in a near monopolist position in the short term and in a dominant position long term. This will, in turn, give the company
pricing power in the industry and the likelihood of superior profits for many years to come. We would expect SHC to
experience substantial ‘overnight’ growth and the returns from this will reward shareholders’ loyalty and significantly
increase the value of the company. Existing shareholders can reasonably expect a significant increase in the value of
their holdings over the very short term and also over the longer term.
Ethical implications of the secrecy option
In addition to the overwhelming business case, however, there is a strong ethical case for the secrecy option. SHC
recognises that it is the moral purpose of SHC to make profits in order to reward those who have risked their own money
to support it over many years. Whilst some companies pursue costly programmes intended to serve multiple stakeholder
interests, SHC recognises that it is required to comply with the demands of its legal owners, its shareholders, and not
to dilute those demands with other concerns that will reduce shareholder returns. This is an important part of the agency
relationship: the SHC board will always serve the best economic interests of its shareholders: its legal owners. The SHC
board believes that any action taken that renders shareholder returns suboptimal is a threat to shareholder value and an
abuse of the agency position. Your board will always seek to maximise shareholder wealth; hence our decision to pursue
the secrecy option in this case. The secrecy option offers the possibility of optimal shareholder value and because
shareholders invest in SHC to maximise returns, that is the only ethical action for the board to pursue. Happily, this
option will also protect the employees’ welfare in SHC’s hometown of Swan Hill and demonstrate its commitment to the
locality. This, in turn, will help to manage two of the key value-adding resources in the company, its employees and its
reputation. This will help in local recruitment and staff retention in future years.
(ii) For the licensing option
Important developments at SHC
Your board was recently faced with a very difficult business and ethical decision. After the discovery by SHC scientists
of the groundbreaking sink production method, we had a choice of keeping the new production technology secret or
sharing the breakthrough under a licensing arrangement with our competitors. After a lengthy discussion, your board
decided that we should pursue the licensing option and I would like to explain our reasons for this on both business and
ethical grounds.
In terms of the business case for licensing, I would like shareholders to understand that although the secrecy option may
have offered SHC the possibility of an unassailable competitive advantage, in reality, it would have incurred a number
of risks. Because of the speed with which we would have needed to have acted, it would have necessitated a large
increase in our borrowing, bringing about a substantial change in our financial structure. This would, in turn, increase
liquidity pressures and make us more vulnerable to rising interest rates. A second risk with the secrecy option would
involve the security of the sink technology ‘secret’. If the sink process was leaked or discovered by competitors and
subsequently copied, our lack of a legally binding patent would mean we would have no legal way to stop them
proceeding with their own version of the sink process.
As well as avoiding the risks, however, the licensing option offers a number of specific business advantages. The royalties
from the licences granted to competitors are expected to be very large indeed. These will be used over the coming years
to extend our existing competitive advantage in the future. Finally, the ‘improvement sharing’ clause in the licensing
contract will ensure that the sink process will be improved and perfected with several manufacturers using the
technology at the same time. SHC’s sink production may, in consequence, improve at a faster rate than would have
been the case were we to have pursued the secrecy option.
Ethical implications of the licensing option
In addition to the business case, there is also a powerful ethical case for the decision we have taken. As a good,
responsible corporate citizen, Swan Hill Company acknowledges its many stakeholders and recognises the impacts that
a business decision has on others. Your board recognises that in addition to external stakeholders having influence over
our operations, our decisions can also affect others. In this case, we have carefully considered the likelihood that keeping
the new technology a secret from our competitors would radically reshape the industry. The superior environmental
performance of the sink process over existing methods will also mean that when fully adopted, the environmental
emissions of the entire industry will be reduced. SHC is very proud of this contribution to this reduction in overall
environmental impact.
There seems little doubt that the secrecy option would have had far-reaching and unfortunate effects upon our industry
and our competitors. The licensing option will allow competitors, and their employees and shareholders, to survive. It
is a compassionate act on our part and shows mercy to the other competitors in the industry. It recognises the number
of impacts that a business decision has and would be the fairest (and most just) option given the number of people
affected. -
第15题:
(b) Discuss ways in which the traditional budgeting process may be seen as a barrier to the achievement of the
aims of EACH of the following models for the implementation of strategic change:
(i) benchmarking;
(ii) balanced scorecard; and
(iii) activity-based models. (12 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Benchmarking
Benchmarks enable goals to be set that may be based on either external measures of ‘best practice’ organisations or internal
cross-functional comparisons which exhibit ‘best practice’. A primary aim of the traditional budgeting process is the setting of
realistic targets that can be achieved within the budget period. The setting of realistic targets means that the extent of
underperformance against ‘best practice’ standards loses visibility, and thus short-term financial targets remain the
predominant focus of the traditional budgeting process. It is arguable that because the budgetary reporting system purports
to give managers ‘control’, there is very little real incentive to seek out benchmarks which may be used to raise budgeted
performance targets. Much depends upon the prevailing organisational culture since benchmarking may be viewed as an
attempt by top management to impose impossible targets upon operational managers. The situation is further exacerbated
where organisations do not measure their success relative to their competition.
Balanced scorecard
The Balanced scorecard is often misunderstood as a consequence of the failure by top management to ensure that it is
implemented effectively within the organisation. Thus it may be viewed as the addition of a few non-financial measures to
the conventional budget. In an attempt to overcome this misperception many management teams now establish a
performance-rewards linkage based upon the achievement of Scorecard targets for the forthcoming budget period.
Unfortunately this can precipitate dysfunctional behaviour at every level within the organisation.
Even in situations where the Scorecard has been well-designed and well-implemented it is difficult for it to gain widespread
acceptance. This is because all too often there exists a culture which places a very high value upon the achievement of the
fixed annual targets in order to avoid the loss of status, recognition and rewards.
A well-constructed Scorecard contains a mix of long-term and short-term measures and therefore drives the company in the
direction of medium-term strategic goals which are supported by cross-functional initiatives. On the other hand, the budgeting
process focuses the organisation on the achievement of short-term financial goals supported by the initiatives of individual
departments. Budgets can also act as an impediment to the acceptance of responsibility by local managers for the
achievement of the Scorecard targets. This is often the case in situations where a continued emphasis exists on meeting shortterm
e.g. quarterly targets.
Activity-based models
Traditional budgets show the costs of functions and departments (e.g. staff costs and establishment costs) instead of the costs
of those activities that are performed by people (e.g. receipt of goods inwards, processing and dispatch of orders etc). Thus
managers have no visibility of the real ‘cost drivers’ of their business. In addition, it is probable that a traditional budget
contains a significant amount of non-value-added costs that are not visible to the managers. The annual budget also tends
to fix capacity for the forthcoming budget period thereby undermining the potential of Activity-based management (ABM)
analysis to determine required capacity from a customer demand perspective. Those experienced in the use of ABM
techniques are used to dealing with such problems, however their tasks would be much easier to perform. and their results
made more reliable if these problems were removed. -
第16题:
(b) Identify and discuss the appropriateness of the cost drivers of any TWO expense values in EACH of levels (i)
to (iii) above and ONE value that relates to level (iv).
In addition, suggest a likely cause of the cost driver for any ONE value in EACH of levels (i) to (iii), and
comment on possible benefits from the identification of the cause of each cost driver. (10 marks)
正确答案:
(b) A cost driver is the factor that determines the level of resource required for an activity. This may be illustrated by considering
costs for each of the four levels in Order Number 377.
Unit based costs:
Direct material costs are driven by the quantity, range, quality and price of materials required per product unit according to
the specification for the order.
Direct labour costs are driven by the number of hours required per product unit and the rate per hour that has been agreed
for each labour grade.
Batch related costs:
The number of machine set-ups per batch is the cost driver for machines used.
The number of design hours per batch is the cost driver for design work.
Product sustaining costs:
The number of marketing visits to a client per order is the cost driver for marketing cost chargeable to the order.
The number of hours of production line maintenance per order is the cost driver for production line cost.
Business sustaining costs:
These costs are absorbed at a rate of 30% of total cost excluding business sustaining costs. This is an arbitrary rate which
indicates the difficulty in identifying a suitable cost driver/drivers for the range of residual costs in this category. Wherever
possible efforts should be made to identify aspects of this residual cost that can be added to the unit, batch or product related
analysis.
The cost drivers are useful in that they provide a basis for an accurate allocation of the cost of resources consumed by an
order. In addition, investigation of the cause(s) of a cost driver occurring at its present level allows action to be considered
that will lead to a reduction in the cost per unit of cost driver.
Examples of causes that might be identified are:
Material price may be higher than necessary due to inefficient sourcing of materials. This may be overcome through efforts
to review sourcing policy and possibly provide additional training to staff responsible for the sourcing of materials.
The number of machine set-ups per batch may be due to lack of planning of batch sizes. It may be possible for batch sizes
in this order to be increased to 1,250 units which would reduce the number of batches required to fulfil the order from five
to four. This should reduce overall costs.
The amount of production line maintenance (and hence cost) required per order may be reduced by examining causes such
as level of skill of maintenance carried out – by GMB’s own staff or out-sourced provision. Action would involve re-training of
own staff or recruitment of new staff or changing of out-source providers.
(alternative relevant examples and discussion would be acceptable for all aspects of part (b)) -
第17题:
(iii) Whether or not you agree with the statement of the marketing director in note (9) above. (5 marks)
Professional marks for appropriateness of format, style. and structure of the report. (4 marks)
正确答案:(iii) The marketing director is certainly correct in recognising that success is dependent on levels of service quality provided
by HFG to its clients. However, whilst the number of complaints is an important performance measure, it needs to be
used with caution. The nature of a complaint is, very often, far more indicative of the absence, or a lack, of service
quality. For example, the fact that 50 clients complained about having to wait for a longer time than they expected to
access gymnasium equipment is insignificant when compared to an accident arising from failure to maintain properly a
piece of gymnasium equipment. Moreover, the marketing director ought to be aware that the absolute number of
complaints may be misleading as much depends on the number of clients serviced during any given period. Thus, in
comparing the number of complaints received by the three centres then a relative measure of complaints received per
1,000 client days would be far more useful than the absolute number of complaints received.
The marketing director should also be advised that the number of complaints can give a misleading picture of the quality
of service provision since individuals have different levels of willingness to complain in similar situations.
The marketing director seems to accept the current level of complaints but is unwilling to accept any increase above this
level. This is not indicative of a quality-oriented organisation which would seek to reduce the number of complaints over
time via a programme of ‘continuous improvement’.
From the foregoing comments one can conclude that it would be myopic to focus on the number of client complaints
as being the only performance measure necessary to measure the quality of service provision. Other performance
measures which may indicate the level of service quality provided to clients by HFG are as follows:
– Staff responsiveness assumes critical significance in service industries. Hence the time taken to resolve client
queries by health centre staff is an important indicator of the level of service quality provided to clients.
– Staff appearance may be viewed as reflecting the image of the centres.
– The comfort of bedrooms and public rooms including facilities such as air-conditioning, tea/coffee-making and cold
drinks facilities, and office facilities such as e-mail, facsimile and photocopying.
– The availability of services such as the time taken to gain an appointment with a dietician or fitness consultant.
– The cleanliness of all areas within the centres will enhance the reputation of HFG. Conversely, unclean areas will
potentially deter clients from making repeat visits and/or recommendations to friends, colleagues etc.
– The presence of safety measures and the frequency of inspections made regarding gymnasium equipment within
the centres and compliance with legislation are of paramount importance in businesses like that of HFG.
– The achievement of target reductions in weight that have been agreed between centre consultants and clients.
(Other relevant measures would be acceptable.)
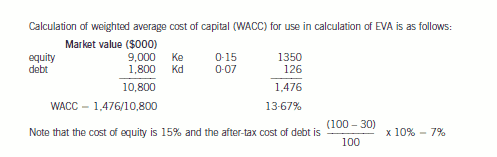
-
第18题:
(iii) State any disadvantages to the relief in (i) that Sharon should be aware of, and identify and describe
another relief that she might use. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(iii) There are several disadvantages to incorporation relief as follows:
1. The requirement to transfer all business assets to the company means that it will not be possible to leave behind
certain assets, such as the property. This might lead to a double tax charge (sale of the property, then extraction
of sale proceeds) at a future date.
2. Taper relief is lost on the transfer of the business. This means that any disposal of chargeable business assets (the
shares) within two years of the incorporation will lead to a higher chargeable gain, as the full rate of business asset
taper relief will not be available.
3. The relief does not eliminate the tax charge, it merely defers the payment of tax until some future event. The
deferred gain will become taxable when Sharon sells her shares in the company.
Gift relief could be used instead of incorporation relief. The assets would be gifted to the company for no consideration,
with the base cost of the assets to the company being reduced by the deferred gain arising. Unlike incorporation relief,
gift relief applies to individual assets used in a trade and not to an entire business. This is particularly useful if the
transferor wishes to retain some assets, such as property outside the company, as not all assets have to be transferred.
Note: If the business was non-trading, incorporation relief would still be available, but gift relief would not. However,
this restriction should not apply to Sharon and gift relief remains an option in this case. -
第19题:
(iii) State how your answer in (ii) would differ if the sale were to be delayed until August 2006. (3 marks)
正确答案:
-
第20题:
(iii) The extent to which Amy will be subject to income tax in the UK on her earnings in respect of duties
performed for Cutlass Inc and the travel costs paid for by that company. (5 marks)
Appropriateness of format and presentation of the report and the effectiveness with which its advice is
communicated. (2 marks)
Note:
You should assume that the income tax rates and allowances for the tax year 2006/07 and the corporation tax
rates and allowances for the financial year 2006 apply throughout this questio
正确答案:
(iii) Amy’s UK income tax position
Amy will remain UK resident and ordinarily resident as she is not leaving the UK permanently or for a complete tax year
under a full time contract of employment. Accordingly, she will continue to be subject to UK tax on her worldwide income
including her earnings in respect of the duties she performs for Cutlass Inc. The earnings from these duties will also be
taxable in Sharpenia as the income arises in that country.
The double tax treaty between the UK and Sharpenia will either exempt the employment income in one of the two
countries or give double tax relief for the tax paid in Sharpenia. The double tax relief will be the lower of the UK tax and
the Sharpenian tax on the income from Cutlass Inc.
Amy will not be subject to UK income tax on the expenses borne by Cutlass Inc in respect of her flights to and from
Sharpenia provided her journeys are wholly and exclusively for the purposes of performing her duties in Sharpenia.
The amounts paid by Cutlass Inc in respect of Amy’s family travelling to Sharpenia will be subject to UK income tax as
Amy will not be absent from the UK for a continuous period of at least 60 days. -
第21题:
In relation to company law, explain:
(a) the limitations on the use of company names; (4 marks)
(b) the tort of ‘passing off’; (4 marks)
(c) the role of the company names adjudicators under the Companies Act 2006. (2 marks)
正确答案:(a) Except in relation to specifically exempted companies, such as those involved in charitable work, companies are required to indicate that they are operating on the basis of limited liability. Thus private companies are required to end their names, either with the word ‘limited’ or the abbreviation ‘ltd’, and public companies must end their names with the words ‘public limited company’ or the abbreviation ‘plc’. Welsh companies may use the Welsh language equivalents (Companies Act (CA)2006 ss.58, 59 & 60).
Companies Registry maintains a register of business names, and will refuse to register any company with a name that is the same as one already on that index (CA 2006 s.66).
Certain categories of names are, subject to the decision of the Secretary of State, unacceptable per se, as follows:
(i) names which in the opinion of the Secretary of State constitute a criminal offence or are offensive (CA 2006 s.53)
(ii) names which are likely to give the impression that the company is connected with either government or local government authorities (s.54).
(iii) names which include a word or expression specified under the Company and Business Names Regulations 1981 (s.26(2)(b)). This category requires the express approval of the Secretary of State for the use of any of the names or expressions contained on the list, and relates to areas which raise a matter of public concern in relation to their use.
Under s.67 of the Companies Act 2006 the Secretary of State has power to require a company to alter its name under the following circumstances:
(i) where it is the same as a name already on the Registrar’s index of company names.
(ii) where it is ‘too like’ a name that is on that index.
The name of a company can always be changed by a special resolution of the company so long as it continues to comply with the above requirements (s.77).(b) The tort of passing off was developed to prevent one person from using any name which is likely to divert business their way by suggesting that the business is actually that of some other person or is connected in any way with that other business. It thus enables people to protect the goodwill they have built up in relation to their business activity. In Ewing v Buttercup
Margarine Co Ltd (1917) the plaintiff successfully prevented the defendants from using a name that suggested a link with
his existing dairy company. It cannot be used, however, if there is no likelihood of the public being confused, where for example the companies are conducting different businesses (Dunlop Pneumatic Tyre Co Ltd v Dunlop Motor Co Ltd (1907)
and Stringfellow v McCain Foods GB Ltd (1984). Nor can it be used where the name consists of a word in general use (Aerators Ltd v Tollitt (1902)).
Part 41 of the Companies Act (CA) 2006, which repeals and replaces the Business Names Act 1985, still does not prevent one business from using the same, or a very similar, name as another business so the tort of passing off will still have an application in the wider business sector. However the Act introduced a new procedure to deal specifically with company names. As previously under the CA 1985, a company cannot register with a name that was the same as any already registered (s.665 Companies Act (CA) 2006) and under CA s.67 the Secretary of State may direct a company to change its name if it has been registered in a name that is the same as, or too like a name appearing on the registrar’s index of company names. In addition, however, a completely new system of complaint has been introduced.(c) Under ss.69–74 of CA 2006 a new procedure has been introduced to cover situations where a company has been registered with a name
(i) that it is the same as a name associated with the applicant in which he has goodwill, or
(ii) that it is sufficiently similar to such a name that its use in the United Kingdom would be likely to mislead by suggesting a connection between the company and the applicant (s.69).
Section 69 can be used not just by other companies but by any person to object to a company names adjudicator if a company’s name is similar to a name in which the applicant has goodwill. There is list of circumstances raising a presumption that a name was adopted legitimately, however even then, if the objector can show that the name was registered either, to obtain money from them, or to prevent them from using the name, then they will be entitled to an order to require the company to change its name.
Under s.70 the Secretary of State is given the power to appoint company names adjudicators and their staff and to finance their activities, with one person being appointed Chief Adjudicator.
Section 71 provides the Secretary of State with power to make rules for the proceedings before a company names adjudicator.
Section 72 provides that the decision of an adjudicator and the reasons for it, are to be published within 90 days of the decision.
Section 73 provides that if an objection is upheld, then the adjudicator is to direct the company with the offending name to change its name to one that does not similarly offend. A deadline must be set for the change. If the offending name is not changed, then the adjudicator will decide a new name for the company.
Under s.74 either party may appeal to a court against the decision of the company names adjudicator. The court can either uphold or reverse the adjudicator’s decision, and may make any order that the adjudicator might have made. -
第22题:
4 (a) ISA 701 Modifications to The Independent Auditor’s Report includes ‘suggested wording of modifying phrases
for use when issuing modified reports’.
Required:
Explain and distinguish between each of the following terms:
(i) ‘qualified opinion’;
(ii) ‘disclaimer of opinion’;
(iii) ‘emphasis of matter paragraph’. (6 marks)
正确答案:
4 PETRIE CO
(a) Independent auditor’s report terms
(i) Qualified opinion – A qualified opinion is expressed when the auditor concludes that an unqualified opinion cannot be
expressed but that the effect of any disagreement with management, or limitation on scope is not so material and
pervasive as to require an adverse opinion or a disclaimer of opinion.
(ii) Disclaimer of opinion – A disclaimer of opinion is expressed when the possible effect of a limitation on scope is so
material and pervasive that the auditor has not been able to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence and accordingly
is unable to express an opinion on the financial statements.
(iii) Emphasis of matter paragraph – An auditor’s report may be modified by adding an emphasis of matter paragraph to
highlight a matter affecting the financial statements that is included in a note to the financial statements that more
extensively discusses the matter. Such an emphasis of matter paragraph does not affect the auditor’s opinion. An
emphasis of matter paragraph may also be used to report matters other than those affecting the financial statements
(e.g. if there is a misstatement of fact in other information included in documents containing audited financial
statements).
(iii) is clearly distinguishable from (i) and (ii) because (i) and (ii) affect the opinion paragraph, whereas (iii) does not.
(i) and (ii) are distinguishable by the degree of their impact on the financial statements. In (i) the effects of any disagreement
or limitation on scope can be identified with an ‘except for …’ opinion. In (ii) the matter is pervasive, that is, affecting the
financial statements as a whole.
(ii) can only arise in respect of a limitation in scope (i.e. insufficient evidence) that has a pervasive effect. (i) is not pervasive
and may also arise from disagreement (i.e. where there is sufficient evidence). -
第23题:
2 (a) Define the following terms:
(i) Forensic Accounting;
(ii) Forensic Investigation;
(iii) Forensic Auditing. (6 marks)
正确答案:
2 Crocus Co
(a) (i) Forensic accounting utilises accounting, auditing, and investigative skills to conduct an examination into a company’s
financial statements. The aim of forensic accounting is to provide an accounting analysis that is potentially suitable for
use in court. Forensic accounting is an umbrella term encompassing both forensic investigations and forensic audits. It
includes the audit of financial information to prove or disprove a fraud, the interview process used during an
investigation, and the act of serving as an expert witness.
Tutorial note: Forensic accounting can be used in a very wide range of situations, e.g. settling monetary disputes in
relation to a business closure, marriage break up, insurance claim, etc. Credit will be awarded for any reasonable
examples provided.
(ii) A forensic investigation is a process whereby a forensic accountant carries out procedures to gather evidence, which
could ultimately be used in legal proceedings or to settle disputes. This could include, for example, an investigation into
money laundering. A forensic investigation involves many stages (similar to an audit), including planning, evidence
gathering, quality control reviews, and finally results in the production of a report.
(iii) Forensic auditing is the specific use of audit procedures within a forensic investigation to find facts and gather evidence,
usually focused on the quantification of a financial loss. This could include, for example, the use of analytical
procedures, and substantive procedures to determine the amount of an insurance claim.
