(b) Describe the potential benefits for Hugh Co in choosing to have a financial statement audit. (4 marks)
题目
(b) Describe the potential benefits for Hugh Co in choosing to have a financial statement audit. (4 marks)
相似考题
更多“(b) Describe the potential benefits for Hugh Co in choosing to have a financial statement audit. (4 marks)”相关问题
-
第1题:
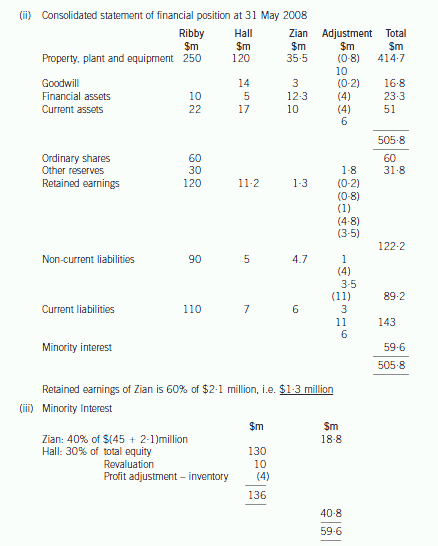
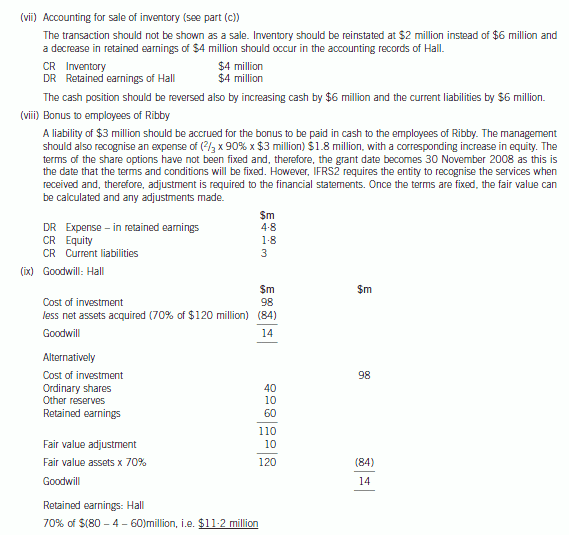
(b) Prepare a consolidated statement of financial position of the Ribby Group at 31 May 2008 in accordance
with International Financial Reporting Standards. (35 marks)
正确答案:




-
第2题:
(b) Discuss the relative costs to the preparer and benefits to the users of financial statements of increased
disclosure of information in financial statements. (14 marks)
Quality of discussion and reasoning. (2 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Increased information disclosure benefits users by reducing the likelihood that they will misallocate their capital. This is
obviously a direct benefit to individual users of corporate reports. The disclosure reduces the risk of misallocation of capital
by enabling users to improve their assessments of a company’s prospects. This creates three important results.
(i) Users use information disclosed to increase their investment returns and by definition support the most profitable
companies which are likely to be those that contribute most to economic growth. Thus, an important benefit of
information disclosure is that it improves the effectiveness of the investment process.
(ii) The second result lies in the effect on the liquidity of the capital markets. A more liquid market assists the effective
allocation of capital by allowing users to reallocate their capital quickly. The degree of information asymmetry between
the buyer and seller and the degree of uncertainty of the buyer and the seller will affect the liquidity of the market as
lower asymmetry and less uncertainty will increase the number of transactions and make the market more liquid.
Disclosure will affect uncertainty and information asymmetry.
(iii) Information disclosure helps users understand the risk of a prospective investment. Without any information, the user
has no way of assessing a company’s prospects. Information disclosure helps investors predict a company’s prospects.
Getting a better understanding of the true risk could lower the price of capital for the company. It is difficult to prove
however that the average cost of capital is lowered by information disclosure, even though it is logically and practically
impossible to assess a company’s risk without relevant information. Lower capital costs promote investment, which can
stimulate productivity and economic growth.
However although increased information can benefit users, there are problems of understandability and information overload.
Information disclosure provides a degree of protection to users. The benefit is fairness to users and is part of corporate
accountability to society as a whole.
The main costs to the preparer of financial statements are as follows:
(i) the cost of developing and disseminating information,
(ii) the cost of possible litigation attributable to information disclosure,
(iii) the cost of competitive disadvantage attributable to disclosure.
The costs of developing and disseminating the information include those of gathering, creating and auditing the information.
Additional costs to the preparers include training costs, changes to systems (for example on moving to IFRS), and the more
complex and the greater the information provided, the more it will cost the company.
Although litigation costs are known to arise from information disclosure, it does not follow that all information disclosure leads
to litigation costs. Cases can arise from insufficient disclosure and misleading disclosure. Only the latter is normally prompted
by the presentation of information disclosure. Fuller disclosure could lead to lower costs of litigation as the stock market would
have more realistic expectations of the company’s prospects and the discrepancy between the valuation implicit in the market
price and the valuation based on a company’s financial statements would be lower. However, litigation costs do not
necessarily increase with the extent of the disclosure. Increased disclosure could reduce litigation costs.
Disclosure could weaken a company’s ability to generate future cash flows by aiding its competitors. The effect of disclosure
on competitiveness involves benefits as well as costs. Competitive disadvantage could be created if disclosure is made relating
to strategies, plans, (for example, planned product development, new market targeting) or information about operations (for
example, production-cost figures). There is a significant difference between the purpose of disclosure to users and
competitors. The purpose of disclosure to users is to help them to estimate the amount, timing, and certainty of future cash
flows. Competitors are not trying to predict a company’s future cash flows, and information of use in that context is not
necessarily of use in obtaining competitive advantage. Overlap between information designed to meet users’ needs and
information designed to further the purposes of a competitor is often coincidental. Every company that could suffer competitive
disadvantage from disclosure could gain competitive advantage from comparable disclosure by competitors. Published figures
are often aggregated with little use to competitors.
Companies bargain with suppliers and with customers, and information disclosure could give those parties an advantage in
negotiations. In such cases, the advantage would be a cost for the disclosing entity. However, the cost would be offset
whenever information disclosure was presented by both parties, each would receive an advantage and a disadvantage.
There are other criteria to consider such as whether the information to be disclosed is about the company. This is both a
benefit and a cost criterion. Users of corporate reports need company-specific data, and it is typically more costly to obtain
and present information about matters external to the company. Additionally, consideration must be given as to whether the
company is the best source for the information. It could be inefficient for a company to obtain or develop data that other, more
expert parties could develop and present or do develop at present.
There are many benefits to information disclosure and users have unmet information needs. It cannot be known with any
certainty what the optimal disclosure level is for companies. Some companies through voluntary disclosure may have
achieved their optimal level. There are no quantitative measures of how levels of disclosure stand with respect to optimal
levels. Standard setters have to make such estimates as best they can, guided by prudence, and by what evidence of benefits
and costs they can obtain. -
第3题:
5 GE Railways plc (GER) operates a passenger train service in Holtland. The directors have always focused solely on
the use of traditional financial measures in order to assess the performance of GER since it commenced operations
in 1992. The Managing Director of GER has asked you, as a management accountant, for assistance with regard to
the adoption of a balanced scorecard approach to performance measurement within GER.
Required:
(a) Prepare a memorandum explaining the potential benefits and limitations that may arise from the adoption of
a balanced scorecard approach to performance measurement within GER. (8 marks)
正确答案:
(a) To: Board of directors
From: Management Accountant
Date: 8 June 2007
The potential benefits of the adoption of a balanced scorecard approach to performance measurement within GER are as
follows:
A broader business perspective
Financial measures invariably have an inward-looking perspective. The balanced scorecard is wider in its scope and
application. It has an external focus and looks at comparisons with competitors in order to establish what constitutes best
practice and ensures that required changes are made in order to achieve it. The use of the balanced scorecard requires a
balance of both financial and non-financial measures and goals.
A greater strategic focus
The use of the balanced scorecard focuses to a much greater extent on the longer term. There is a far greater emphasis on
strategic considerations. It attempts to identify the needs and wants of customers and the new products and markets. Hence
it requires a balance between short term and long term performance measures.
A greater focus on qualitative aspects
The use of the balanced scorecard attempts to overcome the over-emphasis of traditional measures on the quantifiable aspects
of the internal operations of an organisation expressed in purely financial terms. Its use requires a balance between
quantitative and qualitative performance measures. For example, customer satisfaction is a qualitative performance measure
which is given prominence under the balanced scorecard approach.
A greater focus on longer term performance
The use of traditional financial measures is often dominated by financial accounting requirements, for example, the need to
show fixed assets at their historic cost. Also, they are primarily focused on short-term profitability and return on capital
employed in order to gain stakeholder approval of short term financial reports, the longer term or whole life cycle often being
ignored.
The limitations of a balanced scorecard approach to performance measurement may be viewed as follows:
The balanced scorecard attempts to identify the chain of cause and effect relationships which will provide the stimulus for
the future success of an organisation.
Advocates of a balanced scorecard approach to performance measurement suggest that it can constitute a vital component
of the strategic management process.
However, Robert Kaplan and David Norton, the authors of the balanced scorecard concept concede that it may not be suitable
for all firms. Norton suggests that it is most suitable for firms which have a long lead time between management action and
financial benefit and that it will be less suitable for firms with a short-term focus. However, other flaws can be detected in
the balanced scorecard.
The balanced scorecard promises to outline the theory of the firm by clearly linking the driver/outcome measures in a cause
and effect chain, but this will be difficult if not impossible to achieve.
The precise cause and effect relationships between measures for each of the perspectives on the balanced scorecard will be
complex because the driver and outcome measures for the various perspectives are interlinked. For example, customer
satisfaction may be seen to be a function of several drivers, such as employee satisfaction, manufacturing cycle time and
quality. However, employee satisfaction may in turn be partially driven by customer satisfaction and employee satisfaction
may partially drive manufacturing cycle time. A consequence of this non-linearity of the cause and effect chain (i.e., there is
non-linear relationship between an individual driver and a single outcome measure), is that there must be a question mark
as to the accuracy of any calculated correlations between driver and outcome measures. Allied to this point, any calculated
correlations will be historic. This implies that it will only be possible to determine the accuracy of cause and effect linkages
after the event, which could make the use of the balanced scorecard in dynamic industries questionable. If the market is
undergoing rapid evolution, for example, how meaningful are current measures of customer satisfaction or market share?
These criticisms do not necessarily undermine the usefulness of the balanced scorecard in presenting a more comprehensive
picture of organisational performance but they do raise doubts concerning claims that a balanced scorecard can be
constructed which will outline a clear cause and effect chain between driver and outcome measures and the firm’s financial
objectives. -
第4题:
(b) Describe the principal audit work to be performed in respect of the useful lives of Shire Oil Co’s rig platforms.
(6 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Principal audit work – useful life of rig platforms
Tutorial notes: The platforms are just one item of each rig. Candidates should not be awarded marks here for the matters
to be considered in the assessment of useful lives (since this is illustrated in the scenario). No marks will be awarded for
criticising management for estimating useful lives on a per platform. basis or for audit work on depreciation charges/carrying
amounts unrelated to the determination of useful lives.
■ Review of management’s annual assessment of the useful life of each rig at 31 December 2005 and corroboration of
any information that has led to a change in previous estimates. For example, for the abandoned rig, where useful life
has been assessed to be at an end, obtain:
? weather reports;
? incident report supported by photographs;
? insurance claim, etc.
■ Consider management’s past experience and expertise in estimating useful lives. For example, if all lives initially
assessed as short (c. 15 years) are subsequently lengthened (or long lives consistently shortened) this would suggest
that management is being over (under) prudent in its initial estimates.
■ Review of industry comparatives as published in the annual reports of other oil producers.
■ Comparison of actual maintenance costs against budgeted to confirm that the investment needed in maintenance, to
achieve expected life expectancy, is being made.
■ Comparison of actual output (oil extracted) against budgeted. If actual output is less than budgeted the economic life
of the platform. may be:
? shorter (e.g. because there is less oil to be extracted than originally surveyed); or
? longer (e.g. because the rate of extraction is less than budgeted).
Tutorial note: An increase in actual output can be explained conversely.
■ A review of the results of management’s impairment testing of each rig (i.e. the cash-generating unit of which each
platform. is a part).
■ Recalculations of cash flow projections (based on reasonable and supportable assumptions) discounted at a suitable
pre-tax rate.
Tutorial note: As the rigs will not have readily determinable net selling prices (each one being unique and not available
for sale) any impairment will be assessed by a comparison of value in use against carrying amount.
■ Review of working papers of geologist/quantity surveyor(s) employed by Shire supporting estimations of reserves used
in the determination of useful lives of rigs. -
第5题:
(c) Comment on the matters to be considered in seeking to determine the extent of Indigo Co’s financial loss
resulting from the alleged fraud. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(c) Extent of alleged fraud – Matters to be considered
■ Details reported to police: The managing director may have made some estimate of the possible extent of the fraud in
reporting the chief accountant’s disappearance to the police.
■ The minimum loss (assuming no insurance) would be sales for the three days before he left. If not known (e.g. because
the only record of them was in the cash book) a simple estimate might be 3/20 × total recorded revenue for a typical
month.
■ The pattern of cash bankings extracted from bank statements: A falling trend starting during the year might mark the
time from which the chief accountant began to misappropriate cash.
■ Whether other managers have voiced their suspicions, if any, on the chief accountant’s behaviour. For example, if there
was any marked change in his lifestyle. (what he appeared to spend his money on, the hours he worked, etc).
■ The prior year auditor’s report was unmodified. If this was appropriate the chief accountant’s alleged fraudulent activities
may have only started in the current year.
■ The amount of fidelity insurance cover (i.e. against employees handling cash) that Indigo has taken out to meet any
claim for fraud.
■ The likelihood, if any, of recovering misappropriated amounts. For example, if the chief accountant has assets (e.g. a
house) that can be used to settle Indigo’s claims against him in the event that he is caught/successfully prosecuted. -
第6题:
4 (a) The purpose of ISA 250 Consideration of Laws and Regulations in an Audit of Financial Statements is to
establish standards and provide guidance on the auditor’s responsibility to consider laws and regulations in an
audit of financial statements.
Explain the auditor’s responsibilities for reporting non-compliance that comes to the auditor’s attention
during the conduct of an audit. (5 marks)
正确答案:
4 CLEEVES CO
(a) Reporting non-compliance
Non-compliance refers to acts of omission or commission by the entity being audited, either intentional or unintentional, that
are contrary to the prevailing laws or regulations.
To management
Regarding non-compliance that comes to the auditor’s attention the auditor should, as soon as practicable, either:
■ communicate with those charged with governance; or
■ obtain audit evidence that they are appropriately informed.
However, the auditor need not do so for matters that are clearly inconsequential or trivial and may reach agreement1 in
advance on the nature of such matters to be communicated.
If in the auditor’s judgment the non-compliance is believed to be intentional and material, the auditor should communicate
the finding without delay.
If the auditor suspects that members of senior management are involved in non-compliance, the auditor should report the
matter to the next higher level of authority at the entity, if it exists (e.g. an audit committee or a supervisory board). Where
no higher authority exists, or if the auditor believes that the report may not be acted upon or is unsure as to the person to
whom to report, the auditor would consider seeking legal advice.
To the users of the auditor’s report on the financial statements
If the auditor concludes that the non-compliance has a material effect on the financial statements, and has not been properly
reflected in the financial statements, the auditor expresses a qualified (i.e. ‘except for disagreement’) or an adverse opinion.
If the auditor is precluded by the entity from obtaining sufficient appropriate audit evidence to evaluate whether or not noncompliance
that may be material to the financial statements has (or is likely to have) occurred, the auditor should express a
qualified opinion or a disclaimer of opinion on the financial statements on the basis of a limitation on the scope of the audit.
Tutorial note: For example, if management denies the auditor access to information from which he would be able to assess
whether or not illegal dumping had taken place (and, if so, the extent of it).
If the auditor is unable to determine whether non-compliance has occurred because of limitations imposed by circumstances
rather than by the entity, the auditor should consider the effect on the auditor’s report.
Tutorial note: For example, if new legal requirements have been announced as effective but the detailed regulations are not
yet published.
To regulatory and enforcement authorities
The auditor’s duty of confidentiality ordinarily precludes reporting non-compliance to a third party. However, in certain
circumstances, that duty of confidentiality is overridden by statute, law or by courts of law (e.g. in some countries the auditor
is required to report non-compliance by financial institutions to the supervisory authorities). The auditor may need to seek
legal advice in such circumstances, giving due consideration to the auditor’s responsibility to the public interest. -
第7题:
5 You are the audit manager for three clients of Bertie & Co, a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants. The financial
year end for each client is 30 September 2007.
You are reviewing the audit senior’s proposed audit reports for two clients, Alpha Co and Deema Co.
Alpha Co, a listed company, permanently closed several factories in May 2007, with all costs of closure finalised and
paid in August 2007. The factories all produced the same item, which contributed 10% of Alpha Co’s total revenue
for the year ended 30 September 2007 (2006 – 23%). The closure has been discussed accurately and fully in the
chairman’s statement and Directors’ Report. However, the closure is not mentioned in the notes to the financial
statements, nor separately disclosed on the financial statements.
The audit senior has proposed an unmodified audit opinion for Alpha Co as the matter has been fully addressed in
the chairman’s statement and Directors’ Report.
In October 2007 a legal claim was filed against Deema Co, a retailer of toys. The claim is from a customer who slipped
on a greasy step outside one of the retail outlets. The matter has been fully disclosed as a material contingent liability
in the notes to the financial statements, and audit working papers provide sufficient evidence that no provision is
necessary as Deema Co’s lawyers have stated in writing that the likelihood of the claim succeeding is only possible.
The amount of the claim is fixed and is adequately covered by cash resources.
The audit senior proposes that the audit opinion for Deema Co should not be qualified, but that an emphasis of matter
paragraph should be included after the audit opinion to highlight the situation.
Hugh Co was incorporated in October 2006, using a bank loan for finance. Revenue for the first year of trading is
$750,000, and there are hopes of rapid growth in the next few years. The business retails luxury hand made wooden
toys, currently in a single retail outlet. The two directors (who also own all of the shares in Hugh Co) are aware that
due to the small size of the company, the financial statements do not have to be subject to annual external audit, but
they are unsure whether there would be any benefit in a voluntary audit of the first year financial statements. The
directors are also aware that a review of the financial statements could be performed as an alternative to a full audit.
Hugh Co currently employs a part-time, part-qualified accountant, Monty Parkes, who has prepared a year end
balance sheet and income statement, and who produces summary management accounts every three months.
Required:
(a) Evaluate whether the audit senior’s proposed audit report is appropriate, and where you disagree with the
proposed report, recommend the amendment necessary to the audit report of:
(i) Alpha Co; (6 marks)
正确答案:
5 BERTIE & CO
(a) (i) Alpha Co
The factory closures constitute a discontinued operation per IFRS 5 Non-Current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued
Operations, due to the discontinuance of a separate major component of the business. It is a major component due to
the 10% contribution to revenue in the year to 30 September 2007 and 23% contribution in 2006. It is a separate
business component of the company due to the factories having made only one item, indicating a separate income
generating unit.
Under IFRS 5 there must be separate disclosure on the face of the income statement of the post tax results of the
discontinued operation, and of any profit or loss resulting from the closures. The revenue and costs of the discontinued
operation should be separately disclosed either on the face of the income statement or in the notes to the financial
statements. Cash flows relating to the discontinued operation should also be separately disclosed per IAS 7 Cash Flow
Statements.
In addition, as Alpha Co is a listed company, IFRS 8 Operating Segments requires separate segmental disclosure of
discontinued operations.
Failure to disclose the above information in the financial statements is a material breach of International Accounting
Standards. The audit opinion should therefore be qualified on the grounds of disagreement on disclosure (IFRS 5,
IAS 7 and IFRS 8). The matter is material, but not pervasive, and therefore an ‘except for’ opinion should be issued.
The opinion paragraph should clearly state the reason for the disagreement, and an indication of the financial
significance of the matter.
The audit opinion relates only to the financial statements which have been audited, and the contents of the other
information (chairman’s statement and Directors’ Report) are irrelevant when deciding if the financial statements show
a true and fair view, or are fairly presented.
Tutorial note: there is no indication in the question scenario that Alpha Co is in financial or operational difficulty
therefore no marks are awarded for irrelevant discussion of going concern issues and the resultant impact on the audit
opinion. -
第8题:
3 (a) Financial statements often contain material balances recognised at fair value. For auditors, this leads to additional
audit risk.
Required:
Discuss this statement. (7 marks)
正确答案:
3 Poppy Co
(a) Balances held at fair value are frequently recognised as material items in the statement of financial position. Sometimes it is
required by the financial reporting framework that the measurement of an asset or liability is at fair value, e.g. certain
categories of financial instruments, whereas it is sometimes the entity’s choice to measure an item using a fair value model
rather than a cost model, e.g. properties. It is certainly the case that many of these balances will be material, meaning that
the auditor must obtain sufficient appropriate evidence that the fair value measurement is in accordance with the
requirements of financial reporting standards. ISA 540 (Revised and Redrafted) Auditing Accounting Estimates Including Fair
Value Accounting Estimates and Related Disclosures and ISA 545 Auditing Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures
contain guidance in this area.
As part of the understanding of the entity and its environment, the auditor should gain an insight into balances that are stated
at fair value, and then assess the impact of this on the audit strategy. This will include an evaluation of the risk associated
with the balance(s) recognised at fair value.
Audit risk comprises three elements; each is discussed below in the context of whether material balances shown at fair value
will lead to increased risk for the auditor.
Inherent risk
Many measurements based on estimates, including fair value measurements, are inherently imprecise and subjective in
nature. The fair value assessment is likely to involve significant judgments, e.g. regarding market conditions, the timing of
cash flows, or the future intentions of the entity. In addition, there may be a deliberate attempt by management to manipulate
the fair value to achieve a desired aim within the financial statements, in other words to attempt some kind of window
dressing.
Many fair value estimation models are complicated, e.g. discounted cash flow techniques, or the actuarial calculations used
to determine the value of a pension fund. Any complicated calculations are relatively high risk, as difficult valuation techniques
are simply more likely to contain errors than simple valuation techniques. However, there will be some items shown at fair
value which have a low inherent risk, because the measurement of fair value may be relatively straightforward, e.g. assets
that are regularly bought and sold on open markets that provide readily available and reliable information on the market prices
at which actual exchanges occur.
In addition to the complexities discussed above, some fair value measurement techniques will contain significant
assumptions, e.g. the most appropriate discount factor to use, or judgments over the future use of an asset. Management
may not always have sufficient experience and knowledge in making these judgments.
Thus the auditor should approach some balances recognised at fair value as having a relatively high inherent risk, as their
subjective and complex nature means that the balance is prone to contain an error. However, the auditor should not just
assume that all fair value items contain high inherent risk – each balance recognised at fair value should be assessed for its
individual level of risk.
Control risk
The risk that the entity’s internal monitoring system fails to prevent and detect valuation errors needs to be assessed as part
of overall audit risk assessment. One problem is that the fair value assessment is likely to be performed once a year, outside
the normal accounting and management systems, especially where the valuation is performed by an external specialist.
Therefore, as a non-routine event, the assessment of fair value is likely not to have the same level of monitoring or controls
as a day-to-day business transaction.
However, due to the material impact of fair values on the statement of financial position, and in some circumstances on profit,
management may have made great effort to ensure that the assessment is highly monitored and controlled. It therefore could
be the case that there is extremely low control risk associated with the recognition of fair values.
Detection risk
The auditor should minimise detection risk via thorough planning and execution of audit procedures. The audit team may
lack experience in dealing with the fair value in question, and so would be unlikely to detect errors in the valuation techniques
used. Over-reliance on an external specialist could also lead to errors not being found.
Conclusion
It is true that the increasing recognition of items measured at fair value will in many cases cause the auditor to assess the
audit risk associated with the balance as high. However, it should not be assumed that every fair value item will be likely to
contain a material misstatement. The auditor must be careful to identify and respond to the level of risk for fair value items
on an individual basis to ensure that sufficient and appropriate evidence is gathered, thus reducing the audit risk to an
acceptable level. -
第9题:
(b) (i) Discuss the relationship between the concepts of ‘business risk’ and ‘financial statement risk’; and
(4 marks)
正确答案:
(b) (i) Business risk is defined as a threat which could mean that a business fails to meet an ongoing business objective.
Business risks represent problems which are faced by the management of a business, and these problems should be
identified and assessed for their possible impact on the business.
Financial statement risk is the risk that components of the financial statements could be misstated, through inaccurate
or incomplete recording of transactions or disclosure. Financial statement risks therefore represent potential errors or
deliberate misstatements in the published accounts of a business.
There is usually a direct relationship between business risk and financial statement risk. Generally a business risk, if not
addressed by management, will have an impact on specific components of the financial statements. For example, for
Medix Co, declining demand for metal surgical equipment has been identified as a business risk. An associated financial
statement risk is the potential over-valuation of obsolete inventory.
Sometimes business risks have a more general effect on the financial statements. Weak internal systems and controls
are often identified as a business risk. Inadequacies in systems and controls could lead to errors or misstatements in
any area of the financial statements so auditors would perceive this as a general audit risk factor.
Business risks are often linked to going concern issues, because if a business is failing to meet objectives such as cash
generation, or revenue maximisation, then it may struggle to continue in operational existence. In terms of financial
statement risk, going concern is a very specific issue, and the risk is normally the inadequate disclosure of going concern
problems. In the extreme situation where a business is definitely not a going concern, then the risk is that the financial
statements have been prepared on the wrong basis, as in this case the ‘break up basis’ should be used.
Business risk and financial statement risk concepts can both be used by auditors in order to identify areas of the financial
statements likely to be misstated at the year end. The business risk approach places the auditor ‘in the shoes’ of
management, and therefore provides deeper insight into the operations of the business and generates extensive business
understanding. -
第10题:
(b) (i) Explain the matters you should consider, and the evidence you would expect to find in respect of the
carrying value of the cost of investment of Dylan Co in the financial statements of Rosie Co; and
(7 marks)
正确答案:
(b) (i) Cost of investment on acquisition of Dylan Co
Matters to consider
According to the schedule provided by the client, the cost of investment comprises three elements. One matter to
consider is whether the cost of investment is complete.
It appears that no legal or professional fees have been included in the cost of investment (unless included within the
heading ‘cash consideration’). Directly attributable costs should be included per IFRS 3 Business Combinations, and
there is a risk that these costs may be expensed in error, leading to understatement of the investment.
The cash consideration of $2·5 million is the least problematical component. The only matter to consider is whether the
cash has actually been paid. Given that Dylan Co was acquired in the last month of the financial year it is possible that
the amount had not been paid before the year end, in which case the amount should be recognised as a current liability
on the statement of financial position (balance sheet). However, this seems unlikely given that normally control of an
acquired company only passes to the acquirer on cash payment.
IFRS 3 states that the cost of investment should be recognised at fair value, which means that deferred consideration
should be discounted to present value at the date of acquisition. If the consideration payable on 31 January 2009 has
not been discounted, the cost of investment, and the corresponding liability, will be overstated. It is possible that the
impact of discounting the $1·5 million payable one year after acquisition would be immaterial to the financial
statements, in which case it would be acceptable to leave the consideration at face value within the cost of investment.
Contingent consideration should be accrued if it is probable to be paid. Here the amount is payable if revenue growth
targets are achieved over the next four years. The auditor must therefore assess the probability of the targets being
achieved, using forecasts and projections of Maxwell Co’s revenue. Such information is inherently subjective, and could
have been manipulated, if prepared by the vendor of Maxwell Co, in order to secure the deal and maximise
consideration. Here it will be crucial to be sceptical when reviewing the forecasts, and the assumptions underlying the
data. The management of Rosie Co should have reached their own opinion on the probability of paying the contingent
consideration, but they may have relied heavily on information provided at the time of the acquisition.
Audit evidence
– Agreement of the monetary value and payment dates of the consideration per the client schedule to legal
documentation signed by vendor and acquirer.
– Agreement of $2·5 million paid to Rosie Co’s bank statement and cash book prior to year end. If payment occurs
after year end confirm that a current liability is recognised on the individual company and consolidated statement
of financial position (balance sheet).
– Board minutes approving the payment.
– Recomputation of discounting calculations applied to deferred and contingent consideration.
– Agreement that the discount rate used is pre-tax, and reflects current market assessment of the time value of money
(e.g. by comparison to Rosie Co’s weighted average cost of capital).
– Revenue and profit projections for the period until January 2012, checked for arithmetic accuracy.
– A review of assumptions used in the projections, and agreement that the assumptions are comparable with the
auditor’s understanding of Dylan Co’s business.
Tutorial note: As the scenario states that Chien & Co has audited Dylan Co for several years, it is reasonable to rely on
their cumulative knowledge and understanding of the business in auditing the revenue projections. -
第11题:
Following a competitive tender, your audit firm Cal & Co has just gained a new audit client Tirrol Co. You are the manager in charge of planning the audit work. Tirrol Co’s year end is 30 June 2009 with a scheduled date to complete the audit of 15 August 2009. The date now is 3 June 2009.
Tirrol Co provides repair services to motor vehicles from 25 different locations. All inventory, sales and purchasing systems are computerised, with each location maintaining its own computer system. The software in each location is
the same because the programs were written specifically for Tirrol Co by a reputable software house. Data from each location is amalgamated on a monthly basis at Tirrol Co’s head office to produce management and financial accounts.
You are currently planning your audit approach for Tirrol Co. One option being considered is to re-write Cal & Co’s audit software to interrogate the computerised inventory systems in each location of Tirrol Co (except for head office)
as part of inventory valuation testing. However, you have also been informed that any computer testing will have to be on a live basis and you are aware that July is a major holiday period for your audit firm.
Required:
(a) (i) Explain the benefits of using audit software in the audit of Tirrol Co; (4 marks)
(ii) Explain the problems that may be encountered in the audit of Tirrol Co and for each problem, explain
how that problem could be overcome. (10 marks)
(b) Following a discussion with the management at Tirrol Co you now understand that the internal audit department are prepared to assist with the statutory audit. Specifically, the chief internal auditor is prepared to provide you with documentation on the computerised inventory systems at Tirrol Co. The documentation provides details of the software and shows diagrammatically how transactions are processed through the inventory system. This documentation can be used to significantly decrease the time needed to understand the computer systems and enable audit software to be written for this year’s audit.
Required:
Explain how you will evaluate the computer systems documentation produced by the internal audit
department in order to place reliance on it during your audit. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(a)(i)BenefitsofusingauditsoftwareStandardsystemsatclientThesamecomputerisedsystemsandprogramsasusedinall25branchesofTirrolCo.Thismeansthatthesameauditsoftwarecanbeusedineachlocationprovidingsignificanttimesavingscomparedtothesituationwhereclientsystemsaredifferentineachlocation.UseactualcomputerfilesnotcopiesorprintoutsUseofauditsoftwaremeansthattheTirrolCo’sactualinventoryfilescanbetestedratherthanhavingtorelyonprintoutsorscreenimages.Thelattercouldbeincorrect,byaccidentorbydeliberatemistake.Theauditfirmwillhavemoreconfidencethatthe‘real’fileshavebeentested.TestmoreitemsUseofsoftwarewillmeanthatmoreinventoryrecordscanbetested–itispossiblethatallproductlinescouldbetestedforobsolescenceratherthanasampleusingmanualtechniques.Theauditorwillthereforegainmoreevidenceandhavegreaterconfidencethatinventoryisvaluedcorrectly.CostTherelativecostofusingauditsoftwaredecreasesthemoreyearsthatsoftwareisused.Anycostoverrunsthisyearcouldbeoffsetagainsttheauditfeesinfutureyearswhentheactualexpensewillbeless.(ii)ProblemsontheauditofTirrolTimescale–sixweekreportingdeadline–auditplanningTheauditreportisduetobesignedsixweeksaftertheyearend.Thismeansthattherewillbeconsiderablepressureontheauditortocompleteauditworkwithoutcompromisingstandardsbyrushingprocedures.Thisproblemcanbeovercomebycarefulplanningoftheaudit,useofexperiencedstaffandensuringotherstaffsuchassecondpartnerreviewsarebookedwellinadvance.Timescale–sixweekreportingdeadline–softwareissuesTheauditreportisduetobesignedaboutsixweeksaftertheyearend.Thismeansthatthereislittletimetowriteandtestauditsoftware,letaloneusethesoftwareandevaluatetheresultsoftesting.Thisproblemcanbealleviatedbycarefulplanning.AccesstoTirrolCo’ssoftwareanddatafilesmustbeobtainedassoonaspossibleandworkcommencedontailoringCal&Co’ssoftwarefollowingthis.Specialistcomputerauditstaffshouldbebookedassoonaspossibletoperform.thiswork.FirstyearauditcostsTherelativecostsofanauditinthefirstyearataclienttendtobegreaterduetotheadditionalworkofascertainingclientsystems.ThismeansthatCal&Comayhavealimitedbudgettodocumentsystemsincludingcomputersystems.Thisproblemcanbealleviatedtosomeextentagainbygoodauditplanning.Themanagermustalsomonitortheauditprocesscarefully,ensuringthatanyadditionalworkcausedbytheclientnotprovidingaccesstosystemsinformationincludingcomputersystemsisidentifiedandaddedtothetotalbillingcostoftheaudit.StaffholidaysMostoftheauditworkwillbecarriedoutinJuly,whichisalsothemonthwhenmanyofCal&Costafftaketheirannualholiday.Thismeansthattherewillbeashortageofauditstaff,particularlyasauditworkforTirrolCoisbeingbookedwithlittlenotice.Theproblemcanbealleviatedbybookingstaffassoonaspossibleandthenidentifyinganyshortages.Wherenecessary,staffmaybeborrowedfromotherofficesorevendifferentcountriesonasecondmentbasiswhereshortagesareacute.Non-standardsystemsTirrolCo’scomputersoftwareisnon-standard,havingbeenwrittenspecificallyfortheorganisation.Thismeansthatmoretimewillbenecessarytounderstandthesystemthanifstandardsystemswereused.Thisproblemcanbealleviatedeitherbyobtainingdocumentationfromtheclientorbyapproachingthesoftwarehouse(withTirrolCo’spermission)toseeiftheycanassistwithprovisionofinformationondatastructuresfortheinventorysystems.ProvisionofthisinformationwilldecreasethetimetakentotailorauditsoftwareforuseinTirrolCo.IssuesoflivetestingCal&Cohasbeeninformedthatinventorysystemsmustbetestedonalivebasis.Thisincreasestheriskofaccidentalamendmentordeletionofclientdatasystemscomparedtotestingcopyfiles.Tolimitthepossibilityofdamagetoclientsystems,Cal&CocanconsiderperforminginventorytestingondayswhenTirrolCoisnotoperatinge.g.weekends.Attheworst,backupsofdatafilestakenfromthepreviousdaycanbere-installedwhenCal&Co’stestingiscomplete.ComputersystemsTheclienthas25locations,witheachlocationmaintainingitsowncomputersystem.Itispossiblethatcomputersystemsarenotcommonacrosstheclientduetoamendmentsmadeatthebranchlevel.Thisproblemcanbeovercometosomeextentbyaskingstaffateachbranchwhethersystemshavebeenamendedandfocusingauditworkonmaterialbranches.UsefulnessofauditsoftwareTheuseofauditsoftwareatTirrolCodoesappeartohavesignificantproblemsthisyear.Thismeansthateveniftheauditsoftwareisready,theremaystillbesomeriskofincorrectconclusionsbeingderivedduetolackoftesting,etc.Thisproblemcanbealleviatedbyseriouslyconsideringthepossibilityofusingamanualauditthisyear.Themanagermayneedtoinvestigatewhetheramanualauditisfeasibleandifsowhetheritcouldbecompletedwithinthenecessarytimescalewithminimalauditrisk.(b)RelianceoninternalauditdocumentationTherearetwoissuestoconsider;theabilityofinternalaudittoproducethedocumentationandtheactualaccuracyofthedocumentationitself.Theabilityoftheinternalauditdepartmenttoproducethedocumentationcanbedeterminedby:–Ensuringthatthedepartmenthasstaffwhohaveappropriatequalifications.Provisionofarelevantqualificatione.g.membershipofacomputerrelatedinstitutewouldbeappropriate.–Ensuringthatthisandsimilardocumentationisproducedusingarecognisedplanandthatthedocumentationistestedpriortouse.Theuseofdifferentstaffintheinternalauditdepartmenttoproduceandtestdocumentationwillincreaseconfidenceinitsaccuracy.–Ensuringthatthedocumentationisactuallyusedduringinternalauditworkandthatproblemswithdocumentationarenotedandinvestigatedaspartofthatwork.Beinggivenaccesstointernalauditreportsontheinventorysoftwarewillprovideappropriateevidence.Regardingtheactualdocumentation:–Reviewingthedocumentationtoensurethatitappearslogicalandthattermsandsymbolsareusedconsistentlythroughout.Thiswillprovideevidencethattheflowcharts,etcshouldbeaccurate.–Comparingthedocumentationagainstthe‘live’inventorysystemtoensureitcorrectlyreflectstheinventorysystem.Thiscomparisonwillincludetracingindividualtransactionsthroughtheinventorysystems.–UsingpartofthedocumentationtoamendCal&Co’sauditsoftware,andthenensuringthatthesoftwareprocessesinventorysystemdataaccurately.However,thisstagemaybelimitedduetotheneedtouselivefilesatTirrolCo. -
第12题:
You are an audit manager at Rockwell & Co, a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants. You are responsible for the audit of the Hopper Group, a listed audit client which supplies ingredients to the food and beverage industry worldwide.
The audit work for the year ended 30 June 2015 is nearly complete, and you are reviewing the draft audit report which has been prepared by the audit senior. During the year the Hopper Group purchased a new subsidiary company, Seurat Sweeteners Co, which has expertise in the research and design of sugar alternatives. The draft financial statements of the Hopper Group for the year ended 30 June 2015 recognise profit before tax of $495 million (2014 – $462 million) and total assets of $4,617 million (2014: $4,751 million). An extract from the draft audit report is shown below:
Basis of modified opinion (extract)
In their calculation of goodwill on the acquisition of the new subsidiary, the directors have failed to recognise consideration which is contingent upon meeting certain development targets. The directors believe that it is unlikely that these targets will be met by the subsidiary company and, therefore, have not recorded the contingent consideration in the cost of the acquisition. They have disclosed this contingent liability fully in the notes to the financial statements. We do not feel that the directors’ treatment of the contingent consideration is correct and, therefore, do not believe that the criteria of the relevant standard have been met. If this is the case, it would be appropriate to adjust the goodwill balance in the statement of financial position.
We believe that any required adjustment may materially affect the goodwill balance in the statement of financial position. Therefore, in our opinion, the financial statements do not give a true and fair view of the financial position of the Hopper Group and of the Hopper Group’s financial performance and cash flows for the year then ended in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards.
Emphasis of Matter Paragraph
We draw attention to the note to the financial statements which describes the uncertainty relating to the contingent consideration described above. The note provides further information necessary to understand the potential implications of the contingency.
Required:
(a) Critically appraise the draft audit report of the Hopper Group for the year ended 30 June 2015, prepared by the audit senior.
Note: You are NOT required to re-draft the extracts from the audit report. (10 marks)
(b) The audit of the new subsidiary, Seurat Sweeteners Co, was performed by a different firm of auditors, Fish Associates. During your review of the communication from Fish Associates, you note that they were unable to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence with regard to the breakdown of research expenses. The total of research costs expensed by Seurat Sweeteners Co during the year was $1·2 million. Fish Associates has issued a qualified audit opinion on the financial statements of Seurat Sweeteners Co due to this inability to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence.
Required:
Comment on the actions which Rockwell & Co should take as the auditor of the Hopper Group, and the implications for the auditor’s report on the Hopper Group financial statements. (6 marks)
(c) Discuss the quality control procedures which should be carried out by Rockwell & Co prior to the audit report on the Hopper Group being issued. (4 marks)
正确答案:(a) Critical appraisal of the draft audit report
Type of opinion
When an auditor issues an opinion expressing that the financial statements ‘do not give a true and fair view’, this represents an adverse opinion. The paragraph explaining the modification should, therefore, be titled ‘Basis of Adverse Opinion’ rather than simply ‘Basis of Modified Opinion’.
An adverse opinion means that the auditor considers the misstatement to be material and pervasive to the financial statements of the Hopper Group. According to ISA 705 Modifications to Opinions in the Independent Auditor’s Report, pervasive matters are those which affect a substantial proportion of the financial statements or fundamentally affect the users’ understanding of the financial statements. It is unlikely that the failure to recognise contingent consideration is pervasive; the main effect would be to understate goodwill and liabilities. This would not be considered a substantial proportion of the financial statements, neither would it be fundamental to understanding the Hopper Group’s performance and position.
However, there is also some uncertainty as to whether the matter is even material. If the matter is determined to be material but not pervasive, then a qualified opinion would be appropriate on the basis of a material misstatement. If the matter is not material, then no modification would be necessary to the audit opinion.
Wording of opinion/report
The auditor’s reference to ‘the acquisition of the new subsidiary’ is too vague; the Hopper Group may have purchased a number of subsidiaries which this phrase could relate to. It is important that the auditor provides adequate description of the event and in these circumstances it would be appropriate to name the subsidiary referred to.
The auditor has not quantified the amount of the contingent element of the consideration. For the users to understand the potential implications of any necessary adjustments, they need to know how much the contingent consideration will be if it becomes payable. It is a requirement of ISA 705 that the auditor quantifies the financial effects of any misstatements, unless it is impracticable to do so.
In addition to the above point, the auditor should provide more description of the financial effects of the misstatement, including full quantification of the effect of the required adjustment to the assets, liabilities, incomes, revenues and equity of the Hopper Group.
The auditor should identify the note to the financial statements relevant to the contingent liability disclosure rather than just stating ‘in the note’. This will improve the understandability and usefulness of the contents of the audit report.
The use of the term ‘we do not feel that the treatment is correct’ is too vague and not professional. While there may be some interpretation necessary when trying to apply financial reporting standards to unique circumstances, the expression used is ambiguous and may be interpreted as some form. of disclaimer by the auditor with regard to the correct accounting treatment. The auditor should clearly explain how the treatment applied in the financial statements has departed from the requirements of the relevant standard.
Tutorial note: As an illustration to the above point, an appropriate wording would be: ‘Management has not recognised the acquisition-date fair value of contingent consideration as part of the consideration transferred in exchange for the acquiree, which constitutes a departure from International Financial Reporting Standards.’
The ambiguity is compounded by the use of the phrase ‘if this is the case, it would be appropriate to adjust the goodwill’. This once again suggests that the correct treatment is uncertain and perhaps open to interpretation.
If the auditor wishes to refer to a specific accounting standard they should refer to its full title. Therefore instead of referring to ‘the relevant standard’ they should refer to International Financial Reporting Standard 3 Business Combinations.
The opinion paragraph requires an appropriate heading. In this case the auditors have issued an adverse opinion and the paragraph should be headed ‘Adverse Opinion’.
As with the basis paragraph, the opinion paragraph lacks authority; suggesting that the required adjustments ‘may’ materially affect the financial statements implies that there is a degree of uncertainty. This is not the case; the amount of the contingent consideration will be disclosed in the relevant purchase agreement, so the auditor should be able to determine whether the required adjustments are material or not. Regardless, the sentence discussing whether the balance is material or not is not required in the audit report as to warrant inclusion in the report the matter must be considered material. The disclosure of the nature and financial effect of the misstatement in the basis paragraph is sufficient.
Finally, the emphasis of matter paragraph should not be included in the audit report. An emphasis of matter paragraph is only used to draw attention to an uncertainty/matter of fundamental importance which is correctly accounted for and disclosed in the financial statements. An emphasis of matter is not required in this case for the following reasons:
– Emphasis of matter is only required to highlight matters which the auditor believes are fundamental to the users’ understanding of the business. An example may be where a contingent liability exists which is so significant it could lead to the closure of the reporting entity. That is not the case with the Hopper Group; the contingent liability does not appear to be fundamental.
– Emphasis of matter is only used for matters where the auditor has obtained sufficient appropriate evidence that the matter is not materially misstated in the financial statements. If the financial statements are materially misstated, in this regard the matter would be fully disclosed by the auditor in the basis of qualified/adverse opinion paragraph and no emphasis of matter is necessary.
(b) Communication from the component auditor
The qualified opinion due to insufficient evidence may be a significant matter for the Hopper Group audit. While the possible adjustments relating to the current year may not be material to the Hopper Group, the inability to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence with regard to a material matter in Seurat Sweeteners Co’s financial statements may indicate a control deficiency which the auditor was not aware of at the planning stage and it could indicate potential problems with regard to the integrity of management, which could also indicate a potential fraud. It could also indicate an unwillingness of management to provide information, which could create problems for future audits, particularly if research and development costs increase in future years. If the group auditor suspects that any of these possibilities are true, they may need to reconsider their risk assessment and whether the audit procedures performed are still appropriate.
If the detail provided in the communication from the component auditor is insufficient, the group auditor should first discuss the matter with the component auditor to see whether any further information can be provided. The group auditor can request further working papers from the component auditor if this is necessary. However, if Seurat Sweeteners has not been able to provide sufficient appropriate evidence, it is unlikely that this will be effective.
If the discussions with the component auditor do not provide satisfactory responses to evaluate the potential impact on the Hopper Group, the group auditor may need to communicate with either the management of Seurat Sweeteners or the Hopper Group to obtain necessary clarification with regard to the matter.
Following these procedures, the group auditor needs to determine whether they have sufficient appropriate evidence to draw reasonable conclusions on the Hopper Group’s financial statements. If they believe the lack of information presents a risk of material misstatement in the group financial statements, they can request that further audit procedures be performed, either by the component auditor or by themselves.
Ultimately the group engagement partner has to evaluate the effect of the inability to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence on the audit opinion of the Hopper Group. The matter relates to research expenses totalling $1·2 million, which represents 0·2% of the profit for the year and 0·03% of the total assets of the Hopper Group. It is therefore not material to the Hopper Group’s financial statements. For this reason no modification to the audit report of the Hopper Group would be required as this does not represent a lack of sufficient appropriate evidence with regard to a matter which is material to the Group financial statements.
Although this may not have an impact on the Hopper Group audit opinion, this may be something the group auditor wishes to bring to the attention of those charged with governance. This would be particularly likely if the group auditor believed that this could indicate some form. of fraud in Seurat Sweeteners Co, a serious deficiency in financial reporting controls or if this could create problems for accepting future audits due to management’s unwillingness to provide access to accounting records.
(c) Quality control procedures prior to issuing the audit report
ISA 220 Quality Control for an Audit of Financial Statements and ISQC 1 Quality Control for Firms that Perform. Audits and Reviews of Historical Financial Information, and Other Assurance and Related Services Agreements require that an engagement quality control reviewer shall be appointed for audits of financial statements of listed entities. The audit engagement partner then discusses significant matters arising during the audit engagement with the engagement quality control reviewer.
The engagement quality control reviewer and the engagement partner should discuss the failure to recognise the contingent consideration and its impact on the auditor’s report. The engagement quality control reviewer must review the financial statements and the proposed auditor’s report, in particular focusing on the conclusions reached in formulating the auditor’s report and consideration of whether the proposed auditor’s opinion is appropriate. The audit documentation relating to the acquisition of Seurat Sweeteners Co will be carefully reviewed, and the reviewer is likely to consider whether procedures performed in relation to these balances were appropriate.
Given the listed status of the Hopper Group, any modification to the auditor’s report will be scrutinised, and the firm must be sure of any decision to modify the report, and the type of modification made. Once the engagement quality control reviewer has considered the necessity of a modification, they should consider whether a qualified or an adverse opinion is appropriate in the circumstances. This is an important issue, given that it requires judgement as to whether the matters would be material or pervasive to the financial statements.
The engagement quality control reviewer should ensure that there is adequate documentation regarding the judgements used in forming the final audit opinion, and that all necessary matters have been brought to the attention of those charged with governance.
The auditor’s report must not be signed and dated until the completion of the engagement quality control review.
Tutorial note: In the case of the Hopper Group’s audit, the lack of evidence in respect of research costs is unlikely to be discussed unless the audit engagement partner believes that the matter could be significant, for example, if they suspected the lack of evidence is being used to cover up a financial statements fraud.
-
第13题:
(b) Discuss how management’s judgement and the financial reporting infrastructure of a country can have a
significant impact on financial statements prepared under IFRS. (6 marks)
Appropriateness and quality of discussion. (2 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Management judgement may have a greater impact under IFRS than generally was the case under national GAAP. IFRS
utilises fair values extensively. Management have to use their judgement in selecting valuation methods and formulating
assumptions when dealing with such areas as onerous contracts, share-based payments, pensions, intangible assets acquired
in business combinations and impairment of assets. Differences in methods or assumptions can have a major impact on
amounts recognised in financial statements. IAS1 expects companies to disclose the sensitivity of carrying amounts to the
methods, assumptions and estimates underpinning their calculation where there is a significant risk of material adjustment
to their carrying amounts within the next financial year. Often management’s judgement is that there is no ‘significant risk’
and they often fail to disclose the degree of estimation or uncertainty and thus comparability is affected.
In addition to the IFRSs themselves, a sound financial reporting infrastructure is required. This implies effective corporate
governance practices, high quality auditing standards and practices, and an effective enforcement or oversight mechanism.
Therefore, consistency and comparability of IFRS financial statements will also depend on the robust nature of the other
elements of the financial reporting infrastructure.
Many preparers of financial statements will have been trained in national GAAP and may not have been trained in the
principles underlying IFRS and this can lead to unintended inconsistencies when implementing IFRS especially where the
accounting profession does not have a CPD requirement. Additionally where the regulatory system of a country is not well
developed, there may not be sufficient market information to utilise fair value measurements and thus this could lead to
hypothetical markets being created or the use of mathematical modelling which again can lead to inconsistencies because of
lack of experience in those countries of utilising these techniques. This problem applies to other assessments or estimates
relating to such things as actuarial valuations, investment property valuations, impairment testing, etc.
The transition to IFRS can bring significant improvement to the quality of financial performance and improve comparability
worldwide. However, there are issues still remaining which can lead to inconsistency and lack of comparability with those
financial statements. -
第14题:
(b) The Sarbanes-Oxley Act contains provisions for the attestation (verification) and reporting to shareholders of
internal controls over financial reporting.
Required:
Describe the typical contents of an external report on internal controls. (8 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Internal control statement
The United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) guidelines are to disclose in the annual report as follows:
A statement of management’s responsibility for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting
for the company. This will always include the nature and extent of involvement by the chairman and chief executive, but may
also specify the other members of the board involved in the internal controls over financial reporting. The purpose is for
shareholders to be clear about who is accountable for the controls.
A statement identifying the framework used by management to evaluate the effectiveness of this internal control. This will
usually involve a description of the key metrics, measurement methods (e.g. rates of compliance, fair value measures, etc)
and tolerances allowed within these. Within a rules-based environment, these are likely to be underpinned by law.
Management’s assessment of the effectiveness of this internal control as at the end of the company’s most recent fiscal year.
This may involve reporting on rates of compliance, failures, costs, resources committed and outputs (if measurable) achieved.
A statement that its auditor has issued an attestation report on management’s assessment. Any qualification to the attestation
should be reported in this statement.
Tutorial note: guidance from other corporate governance codes is also acceptable. -
第15题:
Note: requirement (a) includes 4 professional marks.
A central feature of the performance measurement system at TSC is the widespread use of league tables that display
each depot’s performance relative to one another.
Required:
(b) Evaluate the potential benefits and problems associated with the use of ‘league tables’ as a means of
measuring performance. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(b) A central feature of many performance measurement systems is the widespread use of league tables that display each
business unit’s performance relative to one another. In the case of service organisations such as TSC the use of league tables
emphasises the company’s critical success factors of profitability and quality of service by reporting results on a weekly basis
at the depot level. The fact that such league tables are used by management will actively encourage competition, in terms of
performance, among depots. The individual position of a business unit in the league table is keenly observed both by the
manager of that unit and his/her peers.
In theory, performance is transparent. In practice although each depot performs essentially the same function and is subject
to the same modes of measurement, circumstances pertaining to different business units may vary significantly. Some depots
may be situated near to the hub (main distribution centre), some may be located far away and some may be in urban zones
with well developed road networks whilst others may be in remote rural areas. Measuring performance via a league table
makes no allowance whatsoever for these relative differences, hence, inequality is built into the performance measurement
system.
Moreover, depot managers might be held responsible for areas over which they have no formal control. The network nature
of the business suggests that there will be a high degree of interdependence of depots; the depot responsible for collection
will very often not be the depot responsible for delivery. Therefore, it is frequently the case that business may be gained for
which the collecting depot receives the revenue, but for which the delivering depot bears the cost. Obviously this impacts
upon the profit statements of both depots. The formal system might not recognise such difficulties, the corporate view being
that ‘the business needs to be managed’; the depots should therefore see any such anomalies as mild constraints to work
around rather than barriers to break down. In such circumstances delivering depots and collecting depots should discuss such
problems on an informal basis. Such informal discussions are aided by close communications between depots recognising
the interdependencies of the business. -
第16题:
(b) Using the information provided, state the financial statement risks arising and justify an appropriate audit
approach for Indigo Co for the year ending 31 December 2005. (14 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Financial statement risks
Assets
■ There is a very high risk that inventory could be materially overstated in the balance sheet (thereby overstating profit)
because:
? there is a high volume of metals (hence material);
? valuable metals are made more portable;
? subsidy gives an incentive to overstate purchases (and hence inventory);
? inventory may not exist due to lack of physical controls (e.g. aluminium can blow away);
? scrap metal in the stockyard may have zero net realisable value (e.g. iron is rusty and slow-moving);
? quantities per counts not attended by an auditor have increased by a third.
■ Inventory could be otherwise misstated (over or under) due to:
? the weighbridge being inaccurate;
? metal qualities being estimated;
? different metals being mixed up; and
? the lack of an independent expert to identify/measure/value metals.
■ Tangible non-current assets are understated as the parts of the furnaces that require replacement (the linings) are not
capitalised (and depreciated) as separate items but treated as repairs/maintenance/renewals and expensed.
■ Cash may be understated due to incomplete recording of sales.
■ Recorded cash will be overstated if it does not exist (e.g. if it has been stolen).
■ Trade receivables may be understated if cash receipts from credit customers have been misappropriated.
Liabilities
■ The provision for the replacement of the furnace linings is overstated by the amount provided in the current and previous
year (i.e. in its entirety).
Tutorial note: Last replacement was two years ago.
Income statement
■ Revenue will be understated in respect of unrecorded cash sales of salvaged metals and ‘clinker’.
■ Scrap metal purchases (for cash) are at risk of overstatement:
? to inflate the 15% subsidy;
? to conceal misappropriated cash.
■ The income subsidy will be overstated if quantities purchased are overstated and/or overvalued (on the quarterly returns)
to obtain the amount of the subsidy.
■ Cash receipts/payments that were recorded only in the cash book in November are at risk of being unrecorded (in the
absence of cash book postings for November), especially if they are of a ‘one-off’ nature.
Tutorial note: Cash purchases of scrap and sales of salvaged metal should be recorded elsewhere (i.e. in the manual
inventory records). However, a one-off expense (of a capital or revenue nature) could be omitted in the absence of
another record.
■ Expenditure is overstated in respect of the 25% provision for replacing the furnace linings. However, as depreciation
will be similarly understated (as the furnace linings have not been capitalised) there is no risk of material misstatement
to the income statement overall.
Disclosure risk
■ A going concern (‘failure’) risk may arise through the loss of:
? sales revenue (e.g. through misappropriation of salvaged metals and/or cash);
? the subsidy (e.g. if returns are prepared fraudulently);
? cash (e.g. if material amounts stolen).
Any significant doubts about going concern must be suitably disclosed in the notes to the financial statements.
Disclosure risk arises if the requirements of IAS 1 ‘Presentation of Financial Statements’ are not met.
■ Disclosure risk arises if contingent liabilities in connection with the dumping of ‘clinker’ (e.g. for fines and penalties) are
not adequately disclosed in accordance with IAS 37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets’.
Appropriate audit approach
Tutorial note: In explaining why AN audit approach is appropriate for Indigo it can be relevant to comment on the
unsuitability of other approaches.
■ A risk-based approach is suitable because:
? inherent risk is high at the entity and financial assertion levels;
? material errors are likely to arise in inventory where a high degree of subjectivity will be involved (regarding quality
of metals, quantities, net realisable value, etc);
? it directs the audit effort to inventory, purchases, income (sales and subsidy) and other risk areas (e.g. contingent
liabilities).
■ A systems-based/compliance approach is not suited to the risk areas identified because controls are lacking/ineffective
(e.g. over inventory and cash). Also, as the audit appointment was not more than three months ago and no interim
audit has been conducted (and the balance sheet date is only three weeks away) testing controls is likely to be less
efficient than a substantive approach.
■ A detailed substantive/balance sheet approach would be suitable to direct audit effort to the appropriate valuation of
assets (and liabilities) existing at balance sheet date. Principal audit work would include:
? attendance at a full physical inventory count at 31 December 2005;
? verifying cash at bank (through bank confirmation and reconciliation) and in hand (through physical count);
? confirming the accuracy of the quarterly returns to the local authority.
■ A cyclical approach/directional testing is unlikely to be suitable as cycles are incomplete. For example the purchases
cycle for metals is ‘purchase/cash’ rather than ‘purchase/payable/cash’ and there is no independent third party evidence
to compensate for that which would be available if there were trade payables (i.e. suppliers’ statements). Also the cycles
are inextricably inter-related to cash and inventory – amounts of which are subject to high inherent risk.
■ Analytical procedures may be of limited use for substantive purposes. Factors restricting the use of substantive analytical
procedures include:
? fluctuating margins (e.g. as many factors will influence the price at which scrap is purchased and subsequently
sold, when salvaged, sometime later);
? a lack of reliable/historic information on which to make comparisons. -
第17题:
(b) Identify and explain the financial statement risks to be taken into account in planning the final audit.
(12 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Financial statement risks
Tutorial note: Note the timeframe. Financial statements for the year to 30 June 2006 are draft. Certain misstatements
may therefore exist due to year-end procedures not yet having taken place.
Revenue/(Receivables)
■ Revenue has increased by 11·8% ((161·5 – 144·4)/144·4 × 100). Overstatement could arise if rebates due to customers
have not yet been accounted for in full (as they are calculated in arrears). If rebates have still to be accounted for trade
receivables will be similarly overstated.
Materials expense
■ Materials expense has increased by 17·8% ((88.0 – 74·7)/74·7 × 100). This is more than the increase in revenue. This
could be legitimate (e.g. if fuel costs have increased significantly). However, the increase could indicate misclassification
of:
– revenue expenditure (see fall in other expenses below);
– capital expenditure (e.g. on overhauls or major refurbishment) as revenue;
– finance lease payments as operating lease.
Depreciation/amortisation
■ This has fallen by 10·5% ((8·5 – 9·5)/9·5 × 100). This could be valid (e.g. if Yates has significant assets already fully
depreciated or the asset base is lower since last year’s restructuring). However, there is a risk of understatement if, for
example:
– not all assets have been depreciated (or depreciated at the wrong rates, or only for 11 months of the year);
– cost of non-current assets is understated (e.g. due to failure to recognise capital expenditure)1;
– impairment losses have not been recognised (as compared with the prior year).
Tutorial note: Depreciation on vehicles and transport equipment represents only 7% of cost. If all items were being
depreciated on a straight-line basis over eight years this should be 12·5%. The depreciation on other equipment looks more
reasonable as it amounts to 14% which would be consistent with an average age of vehicles of seven years (i.e. in the middle
of the range 3 – 13 years).
Other expenses
■ These have fallen by 15·5% ((19·6 – 23·2)/23·2 × 100). They may have fallen (e.g. following the restructuring) or may be
understated due to:
– expenses being misclassified as materials expense;
– underestimation of accrued expenses (especially as the financial reporting period has not yet expired).
Intangibles
■ Intangible assets have increased by $1m (16% on the prior year). Although this may only just be material to the
financial statements as a whole (see (a)) this is the net movement, therefore additions could be material.
■ Internally-generated intangibles will be overstated if:
– any of the IAS 38 recognition criteria cannot be demonstrated;
– any impairment in the year has not yet been written off in accordance with IAS 36 ‘Impairment of Assets’.
Tangible assets
■ The net book value of property (at cost) has fallen by 5%, vehicles are virtually unchanged (increased by just 2·5%)
and other equipment (though the least material category) has fallen by 20·4%.
■ Vehicles and equipment may be overstated if:
– disposals have not been recorded;
– depreciation has been undercharged (e.g. not for a whole year);
– impairments have not yet been accounted for.
■ Understatement will arise if finance leases are treated as operating leases.
Receivables
■ Trade receivables have increased by just 2·2% (although sales increased by 11·8%) and may be understated due to a
cutoff error resulting in overstatement of cash receipts.
■ There is a risk of overstatement if sufficient allowances have not been made for the impairment of individually significant
balances and for the remainder assessed on a portfolio or group basis.
Restructuring provision
■ The restructuring provision that was made last year has fallen/been utilised by 10·2%. There is a risk of overstatement
if the provision is underutilised/not needed for the purpose for which it was established.
Finance lease liabilities
■ Although finance lease liabilities have increased (by $1m) there is a greater risk of understatement than overstatement
if leased assets are not recognised on the balance sheet (i.e. capitalised).
■ Disclosure risk arises if the requirements of IAS 17 ‘Leases’ (e.g. in respect of minimum lease payments) are not met.
Trade payables
■ These have increased by only 5·3% compared with the 17·8% increase in materials expense. There is a risk of
understatement as notifications (e.g. suppliers’ invoices) of liabilities outstanding at 30 June 2006 may have still to be
received (the month of June being an unexpired period).
Other (employee) liabilities
■ These may be understated as they have increased by only 7·5% although staff costs have increased by 14%. For
example, balances owing in respect of outstanding holiday entitlements at the year end may not yet be accurately
estimated.
Tutorial note: Credit will be given to other financial statements risks specific to the scenario. For example, ‘time-sensitive
delivery schedules’ might give rise to penalties or claims, that could result in understated provisions or undisclosed
contingent liabilities. Also, given that this is a new audit and the result has changed significantly (from loss to profit) might
suggest a risk of misstatement in the opening balances (and hence comparative information).
1 Tutorial note: This may be unlikely as other expenses have fallen also. -
第18题:
(c) Describe the examination procedures you should use to verify Cusiter Co’s prospective financial information.
(9 marks)
正确答案:
(c) Examination procedures
■ The arithmetic accuracy of the PFI should be confirmed, i.e. subtotals and totals should be recast and agreed.
■ The actual information for the year to 31 December 2006 that is shown as comparative information should be agreed
to the audited financial statements for that year to ensure consistency.
■ Balances and transaction totals for the quarter to 31 March 2007 should be agreed to general ledger account balances
at that date. The net book value of property, plant and equipment should be agreed to the non-current asset register;
accounts receivable/payable to control accounts and cash at bank to a bank reconciliation statement.
■ Tenders for the new equipment should be inspected to confirm the additional cost included in property, plant and
equipment included in the forecast for the year to 31 December 2008 and that it can be purchased with the funds being
lent by the bank.
■ The reasonableness of all new assumptions should be considered. For example, the expected useful life of the new
equipment, the capacity at which it will be operating, the volume of new product that can be sold, and at what price.
■ The forecast income statement should be reviewed for completeness of costs associated with the expansion. For
example, operating expenses should include salaries of additional equipment operatives or supervisors.
■ The consistency of accounting practices reflected in the forecast with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
should be considered. For example, the intangible asset might be expected to be less than $10,000 at 31 December
2008 as it should be carried at amortised cost.
■ The cost of property, plant and equipment at 31 December 2008 is $280,000 more than as at 31 December 2007.
Consideration should be given to the adequacy of borrowing $250,000 if the actual investment is $30,000 more.
■ The terms of existing borrowings (both non-current and short-term) should be reviewed to ensure that the forecast takes
full account of existing repayment schedules. For example, to confirm that only $23,000 of term borrowings will become
current by the end of 2007.
Trends should be reviewed and fluctuations explained, for example:
■ Revenue for the first quarter of 2007 is only 22% of revenue for 2006 and so may appear to be understated. However,
revenue may not be understated if sales are seasonal and the first quarter is traditionally ‘quieter’.
■ Forecast revenue for 2007 is 18% up on 2006. However, forecast revenue for 2008 is only 19% up on 2007. As the
growth in 2007 is before the investment in new plant and equipment it does not look as though the new investment
will be contributing significantly to increased growth in the first year.
■ The gross profit % is maintained at around 29% for the three years. However, the earnings before interest and tax (EBIT)
% is forecast to fall by 2% for 2008. Earnings after interest might be worrying to the potential lender as this is forecast
to rise from 12·2% in 2006 to 13·7% in 2007 but then fall to 7·6% in 2008.
The reasonableness of relationships between income statement and balance sheet items should be considered. For example:
■ The average collection period at each of the balance sheet dates presented is 66, 69, 66 and 66 days respectively (e.g.
71/394 × 365 = 66 days). Although it may be realistic to assume that the current average collection period may be
maintained in future it is possible that it could deteriorate if, for example, new customers taken on to launch the new
product are not as credit worthy as the existing customer base.
■ The number of days sales in inventory at each balance sheet date is 66, 88, 66 and 65 days respectively (e.g. 50/278
× 365 = 66 days). The reason for the increase to 88 at the end of the first quarter must be established and
management’s assertion that 66 days will be re-established as the ‘norm’ corroborated.
■ As the $42,000 movement on retained earnings from 2007 to 2008 is the earnings before income tax for 2008 it may
be that there is no tax in 2008 or that tax effects have not been forecast. (However, some deferred tax effect might be
expected if the investment in new plant and equipment is likely to attract accelerated capital allowances.) -
第19题:
(c) With specific reference to Hugh Co, discuss the objective of a review engagement and contrast the level of
assurance provided with that provided in an audit of financial statements. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(c) The objective of a review engagement is to enable the auditor to obtain moderate assurance as to whether the financial
statements have been prepared in accordance with an identified financial reporting framework. This is defined in ISRE 2400
Engagements to Review Financial Statements.
In order to obtain this assurance, it is necessary to gather evidence using analytical procedures and enquiries with
management. Detailed substantive procedures will not be performed unless the auditor has reason to believe that the
information may be materially misstated.
The auditor should approach the engagement with a high degree of professional scepticism, looking for circumstances that
may cause the financial statements to be misstated. For example, in Hugh Co, the fact that the preparer of the financial
statements is part-qualified may lead the auditor to believe that there is a high inherent risk that the figures are misstated.
As a result of procedures performed, the auditor’s objective is to provide a clear written expression of negative assurance on
the financial statements. In a review engagement the auditor would state that ‘we are not aware of any material modifications
that should be made to the financial statements….’
This is normally referred to as an opinion of ‘negative assurance’.
Negative assurance means that the auditor has performed limited procedures and has concluded that the financial statements
appear reasonable. The user of the financial statements gains some comfort that the figures have been subject to review, but
only a moderate level of assurance is provided. The user may need to carry out additional procedures of their own if they
want to rely on the financial statements. For example, if Hugh Co were to use the financial statements as a means to raise
further bank finance, the bank would presumably perform, or require Hugh Co to perform, additional procedures to provide
a higher level of assurance as to the validity of the figures contained in the financial statements.
In comparison, in an audit, a high level of assurance is provided. The auditors provide an opinion of positive, but not absolute
assurance. The user is assured that the figures are free from material misstatement and that the auditor has based the opinion
on detailed procedures. -
第20题:
(b) You are the manager responsible for the audit of Poppy Co, a manufacturing company with a year ended
31 October 2008. In the last year, several investment properties have been purchased to utilise surplus funds
and to provide rental income. The properties have been revalued at the year end in accordance with IAS 40
Investment Property, they are recognised on the statement of financial position at a fair value of $8 million, and
the total assets of Poppy Co are $160 million at 31 October 2008. An external valuer has been used to provide
the fair value for each property.
Required:
(i) Recommend the enquiries to be made in respect of the external valuer, before placing any reliance on their
work, and explain the reason for the enquiries; (7 marks)
正确答案:
(b) (i) Enquiries in respect of the external valuer
Enquiries would need to be made for two main reasons, firstly to determine the competence, and secondly the objectivity
of the valuer. ISA 620 Using the Work of an Expert contains guidance in this area.
Competence
Enquiries could include:
– Is the valuer a member of a recognised professional body, for example a nationally or internationally recognised
institute of registered surveyors?
– Does the valuer possess any necessary licence to carry out valuations for companies?
– How long has the valuer been a member of the recognised body, or how long has the valuer been licensed under
that body?
– How much experience does the valuer have in providing valuations of the particular type of investment properties
held by Poppy Co?
– Does the valuer have specific experience of evaluating properties for the purpose of including their fair value within
the financial statements?
– Is there any evidence of the reputation of the valuer, e.g. professional references, recommendations from other
companies for which a valuation service has been provided?
– How much experience, if any, does the valuer have with Poppy Co?
Using the above enquiries, the auditor is trying to form. an opinion as to the relevance and reliability of the valuation
provided. ISA 500 Audit Evidence requires that the auditor gathers evidence that is both sufficient and appropriate. The
auditor needs to ensure that the fair values provided by the valuer for inclusion in the financial statements have been
arrived at using appropriate knowledge and skill which should be evidenced by the valuer being a member of a
professional body, and, if necessary, holding a licence under that body.
It is important that the fair values have been arrived at using methods allowed under IAS 40 Investment Property. If any
other valuation method has been used then the value recognised in the statement of financial position may not be in
accordance with financial reporting standards. Thus it is important to understand whether the valuer has experience
specifically in providing valuations that comply with IAS 40, and how many times the valuer has appraised properties
similar to those owned by Poppy Co.
In gauging the reliability of the fair value, the auditor may wish to consider how Poppy Co decided to appoint this
particular valuer, e.g. on the basis of a recommendation or after receiving references from companies for which
valuations had previously been provided.
It will also be important to consider how familiar the valuer is with Poppy Co’s business and environment, as a way to
assess the reliability and appropriateness of any assumptions used in the valuation technique.
Objectivity
Enquiries could include:
– Does the valuer have any financial interest in Poppy Co, e.g. shares held directly or indirectly in the company?
– Does the valuer have any personal relationship with any director or employee of Poppy Co?
– Is the fee paid for the valuation service reasonable and a fair, market based price?
With these enquiries, the auditor is gaining assurance that the valuer will perform. the valuation from an independent
point of view. If the valuer had a financial interest in Poppy Co, there would be incentive to manipulate the valuation in
a way best suited to the financial statements of the company. Equally if the valuer had a personal relationship with a
senior member of staff at Poppy Co, the valuer may feel pressured to give a favourable opinion on the valuation of the
properties.
The level of fee paid is important. It should be commensurate with the market rate paid for this type of valuation. If the
valuer was paid in excess of what might be considered a normal fee, it could indicate that the valuer was encouraged,
or even bribed, to provide a favourable valuation. -
第21题:
(ii) Identify and explain the potential financial statement risks caused by the breach of planning regulations
discussed in the press cutting. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Several significant financial statement risks are indicated by the press cutting.
Overstatement of property, plant and equipment
Medix Co has constructed a research laboratory which is likely to be impaired at the year end. The local authority has
the power to shut down the facility, and it is clear from the press cutting that this is likely to happen before the year end.
Following IAS 36 Impairment of Assets, the premises should be written down to recoverable amount, and the
impairment loss recognised as an expense. The directors should carry out an impairment review before the year end. If
the premises cannot be used as intended then the recoverable amount (measured using the higher of value in use and
fair value less selling cost) is likely to be less than current carrying value. In this case, assuming the local authority is
successful in shutting down the research laboratory, the recoverable amount is likely to be nil, as the premises have no
value in use, as it will never be used commercially, and has no market value as it is likely to be demolished.
In addition, any tangible assets such as laboratory equipment located at the premises should be tested for impairment
as if the company cannot use the premises then the assets contained within it are likely to have a lower recoverable
amount than carrying value.
Contingency – fines or penalties imposed by local authority
The press cutting indicates that Medix Co has been sued before, and that the local authority may again take legal action
against the company. IAS 37 Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets states that a provision should be
recognised if the company has a probable obligation at the year end which can be measured reliably. If payment is
deemed only possible at the year end, then disclosure of the contingent liability should be made in a note to the financial
statements.
If the local authority commences legal proceedings against Medix Co before the year end of 30 June 2008, then
management should assess the probability of payment. The financial statement risk is not recognising a provision (and
associated expense within the income statement), or not disclosing a contingency.
Demolition costs
The local authority may require Medix Co to demolish the premises. If this demand is made before the year end, Medix
Co should recognise a provision for demolition costs as an unavoidable legal obligation would have been created. The
financial statement risk is that in this situation, Medix Co fails to recognise a provision and associated expense within
the income statement.
Going concern
The above issues could indicate that the company may not continue in operational existence. The potential lack of
disclosure of these issues represents a financial statement risk. -
第22题:
You are an audit manager responsible for providing hot reviews on selected audit clients within your firm of Chartered
Certified Accountants. You are currently reviewing the audit working papers for Pulp Co, a long standing audit client,
for the year ended 31 January 2008. The draft statement of financial position (balance sheet) of Pulp Co shows total
assets of $12 million (2007 – $11·5 million).The audit senior has made the following comment in a summary of
issues for your review:
‘Pulp Co’s statement of financial position (balance sheet) shows a receivable classified as a current asset with a value
of $25,000. The only audit evidence we have requested and obtained is a management representation stating the
following:
(1) that the amount is owed to Pulp Co from Jarvis Co,
(2) that Jarvis Co is controlled by Pulp Co’s chairman, Peter Sheffield, and
(3) that the balance is likely to be received six months after Pulp Co’s year end.
The receivable was also outstanding at the last year end when an identical management representation was provided,
and our working papers noted that because the balance was immaterial no further work was considered necessary.
No disclosure has been made in the financial statements regarding the balance. Jarvis Co is not audited by our firm
and we have verified that Pulp Co does not own any shares in Jarvis Co.’
Required:
(b) In relation to the receivable recognised on the statement of financial position (balance sheet) of Pulp Co as
at 31 January 2008:
(i) Comment on the matters you should consider. (5 marks)
正确答案:
(b) (i) Matters to consider
Materiality
The receivable represents only 0·2% (25,000/12 million x 100) of total assets so is immaterial in monetary terms.
However, the details of the transaction could make it material by nature.
The amount is outstanding from a company under the control of Pulp Co’s chairman. Readers of the financial statements
would be interested to know the details of this transaction, which currently is not disclosed. Elements of the transaction
could be subject to bias, specifically the repayment terms, which appear to be beyond normal commercial credit terms.
Paul Sheffield may have used his influence over the two companies to ‘engineer’ the transaction. Disclosure is necessary
due to the nature of the transaction, the monetary value is irrelevant.
A further matter to consider is whether this is a one-off transaction, or indicative of further transactions between the two
companies.
Relevant accounting standard
The definitions in IAS 24 must be carefully considered to establish whether this actually constitutes a related party
transaction. The standard specifically states that two entities are not necessarily related parties just because they have
a director or other member of key management in common. The audit senior states that Jarvis Co is controlled by Peter
Sheffield, who is also the chairman of Pulp Co. It seems that Peter Sheffield is in a position of control/significant influence
over the two companies (though this would have to be clarified through further audit procedures), and thus the two
companies are likely to be perceived as related.
IAS 24 requires full disclosure of the following in respect of related party transactions:
– the nature of the related party relationship,
– the amount of the transaction,
– the amount of any balances outstanding including terms and conditions, details of security offered, and the nature
of consideration to be provided in settlement,
– any allowances for receivables and associated expense.
There is currently a breach of IAS 24 as no disclosure has been made in the notes to the financial statements. If not
amended, the audit opinion on the financial statements should be qualified with an ‘except for’ disagreement. In
addition, if practicable, the auditor’s report should include the information that would have been included in the financial
statements had the requirements of IAS 24 been adhered to.
Valuation and classification of the receivable
A receivable should only be recognised if it will give rise to future economic benefit, i.e. a future cash inflow. It appears
that the receivable is long outstanding – if the amount is unlikely to be recovered then it should be written off as a bad
debt and the associated expense recognised. It is possible that assets and profits are overstated.
Although a representation has been received indicating that the amount will be paid to Pulp Co, the auditor should be
sceptical of this claim given that the same representation was given last year, and the amount was not subsequently
recovered. The $25,000 could be recoverable in the long term, in which case the receivable should be reclassified as
a non-current asset. The amount advanced to Jarvis Co could effectively be an investment rather than a short term
receivable. Correct classification on the statement of financial position (balance sheet) is crucial for the financial
statements to properly show the liquidity position of the company at the year end.
Tutorial note: Digressions into management imposing a limitation in scope by withholding evidence are irrelevant in this
case, as the scenario states that the only evidence that the auditors have asked for is a management representation.
There is no indication in the scenario that the auditors have asked for, and been refused any evidence. -
第23题:
(a) Contrast the role of internal and external auditors. (8 marks)
(b) Conoy Co designs and manufactures luxury motor vehicles. The company employs 2,500 staff and consistently makes a net profit of between 10% and 15% of sales. Conoy Co is not listed; its shares are held by 15 individuals, most of them from the same family. The maximum shareholding is 15% of the share capital.
The executive directors are drawn mainly from the shareholders. There are no non-executive directors because the company legislation in Conoy Co’s jurisdiction does not require any. The executive directors are very successful in running Conoy Co, partly from their training in production and management techniques, and partly from their ‘hands-on’ approach providing motivation to employees.
The board are considering a significant expansion of the company. However, the company’s bankers are
concerned with the standard of financial reporting as the financial director (FD) has recently left Conoy Co. The board are delaying provision of additional financial information until a new FD is appointed.
Conoy Co does have an internal audit department, although the chief internal auditor frequently comments that the board of Conoy Co do not understand his reports or provide sufficient support for his department or the internal control systems within Conoy Co. The board of Conoy Co concur with this view. Anders & Co, the external auditors have also expressed concern in this area and the fact that the internal audit department focuses work on control systems, not financial reporting. Anders & Co are appointed by and report to the board of Conoy Co.
The board of Conoy Co are considering a proposal from the chief internal auditor to establish an audit committee.
The committee would consist of one executive director, the chief internal auditor as well as three new appointees.
One appointee would have a non-executive seat on the board of directors.
Required:
Discuss the benefits to Conoy Co of forming an audit committee. (12 marks)
正确答案:
(a)Roleofinternalandexternalauditors–differencesObjectivesThemainobjectiveofinternalauditistoimproveacompany’soperations,primarilyintermsofvalidatingtheefficiencyandeffectivenessoftheinternalcontrolsystemsofacompany.Themainobjectiveoftheexternalauditoristoexpressanopiniononthetruthandfairnessofthefinancialstatements,andotherjurisdictionspecificrequirementssuchasconfirmingthatthefinancialstatementscomplywiththereportingrequirementsincludedinlegislation.ReportingInternalauditreportsarenormallyaddressedtotheboardofdirectors,orotherpeoplechargedwithgovernancesuchastheauditcommittee.Thosereportsarenotpubliclyavailable,beingconfidentialbetweentheinternalauditorandtherecipient.Externalauditreportsareprovidedtotheshareholdersofacompany.Thereportisattachedtotheannualfinancialstatementsofthecompanyandisthereforepubliclyavailabletotheshareholdersandanyreaderofthefinancialstatements.ScopeofworkTheworkoftheinternalauditornormallyrelatestotheoperationsoftheorganisation,includingthetransactionprocessingsystemsandthesystemstoproducetheannualfinancialstatements.Theinternalauditormayalsoprovideotherreportstomanagement,suchasvalueformoneyauditswhichexternalauditorsrarelybecomeinvolvedwith.Theworkoftheexternalauditorrelatesonlytothefinancialstatementsoftheorganisation.However,theinternalcontrolsystemsoftheorganisationwillbetestedastheseprovideevidenceonthecompletenessandaccuracyofthefinancialstatements.RelationshipwithcompanyInmostorganisations,theinternalauditorisanemployeeoftheorganisation,whichmayhaveanimpactontheauditor’sindependence.However,insomeorganisationstheinternalauditfunctionisoutsourced.Theexternalauditorisappointedbytheshareholdersofanorganisation,providingsomedegreeofindependencefromthecompanyandmanagement.(b)BenefitsofauditcommitteeinConoyCoAssistancewithfinancialreporting(nofinanceexpertise)TheexecutivedirectorsofConoyCodonotappeartohaveanyspecificfinancialskills–asthefinancialdirectorhasrecentlyleftthecompanyandhasnotyetbeenreplaced.ThismaymeanthatfinancialreportinginConoyCoislimitedorthattheothernon-financialdirectorsspendasignificantamountoftimekeepinguptodateonfinancialreportingissues.AnauditcommitteewillassistConoyCobyprovidingspecialistknowledgeoffinancialreportingonatemporarybasis–atleastoneofthenewappointeesshouldhaverelevantandrecentfinancialreportingexperienceundercodesofcorporategovernance.ThiswillallowtheexecutivedirectorstofocusonrunningConoyCo.EnhanceinternalcontrolsystemsTheboardofConoyCodonotnecessarilyunderstandtheworkoftheinternalauditor,ortheneedforcontrolsystems.ThismeansthatinternalcontrolwithinConoyComaybeinadequateorthatemployeesmaynotrecognisetheimportanceofinternalcontrolsystemswithinanorganisation.TheauditcommitteecanraiseawarenessoftheneedforgoodinternalcontrolsystemssimplybybeingpresentinConoyCoandbyeducatingtheboardontheneedforsoundcontrols.Improvingtheinternalcontrol‘climate’willensuretheneedforinternalcontrolsisunderstoodandreducecontrolerrors.RelianceonexternalauditorsConoyCo’sinternalauditorscurrentlyreporttotheboardofConoyCo.Aspreviouslynoted,thelackoffinancialandcontrolexpertiseontheboardwillmeanthatexternalauditorreportsandadvicewillnotnecessarilybeunderstood–andtheboardmayrelytoomuchonexternalauditorsIfConoyCoreporttoanauditcommitteethiswilldecreasethedependenceoftheboardontheexternalauditors.Theauditcommitteecantaketimetounderstandtheexternalauditor’scomments,andthenviathenon-executivedirector,ensurethattheboardtakeactiononthosecomments.AppointmentofexternalauditorsAtpresent,theboardofConoyCoappointtheexternalauditors.Thisraisesissuesofindependenceastheboardmaybecometoofamiliarwiththeexternalauditorsandsoappointonthisfriendshipratherthanmerit.Ifanauditcommitteeisestablished,thenthiscommitteecanrecommendtheappointmentoftheexternalauditors.Thecommitteewillhavethetimeandexpertisetoreviewthequalityofserviceprovidedbytheexternalauditors,removingtheindependenceissue.Corporategovernancerequirements–bestpracticeConoyCodonotneedtofollowcorporategovernancerequirements(thecompanyisnotlisted).However,notfollowingthoserequirementsmaystarttohaveadverseeffectsonConoy.Forexample,ConoyCo’sbankisalreadyconcernedaboutthelackoftransparencyinreporting.EstablishinganauditcommitteewillshowthattheboardofConoyCoarecommittedtomaintainingappropriateinternalsystemsinthecompanyandprovidingthestandardofreportingexpectedbylargecompanies.Obtainingthenewbankloanshouldalsobeeasierasthebankwillbesatisfiedwithfinancialreportingstandards.Givennonon-executives–independentadvicetoboardCurrentlyConoyCodoesnothaveanynon-executivedirectors.Thismeansthatthedecisionsoftheexecutivedirectorsarenotbeingchallengedbyotherdirectorsindependentofthecompanyandwithlittleornofinancialinterestinthecompany.Theappointmentofanauditcommitteewithonenon-executivedirectorontheboardofConoyCowillstarttoprovidesomenon-executiveinputtoboardmeetings.Whilenotsufficientintermsofcorporategovernancerequirements(aboutequalnumbersofexecutiveandnon-executivedirectorsareexpected)itdoesshowtheboardofConoyCoareattemptingtoestablishappropriategovernancesystems.AdviceonriskmanagementFinally,thereareothergeneralareaswhereConoyCowouldbenefitfromanauditcommittee.Forexample,lackofcorporategovernancestructuresprobablymeansConoyCodoesnothaveariskmanagementcommittee.Theauditcommitteecanalsoprovideadviceonriskmanagement,helpingtodecreasetheriskexposureofthecompany.
