(a) The following information relates to Crosswire a publicly listed company.Summarised statements of financial position as at:The following information is available:(i) During the year to 30 September 2009, Crosswire embarked on a replacement and expansi
题目
(a) The following information relates to Crosswire a publicly listed company.
Summarised statements of financial position as at:
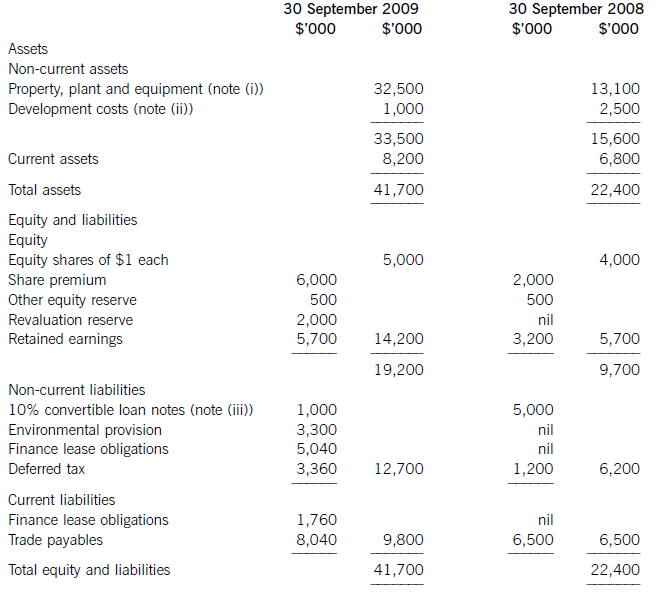
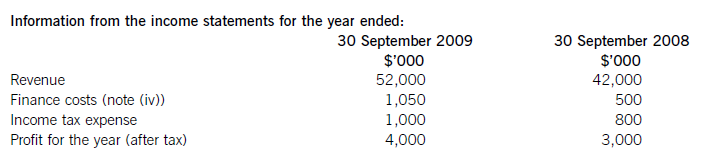
The following information is available:
(i) During the year to 30 September 2009, Crosswire embarked on a replacement and expansion programme for its non-current assets. The details of this programme are:
On 1 October 2008 Crosswire acquired a platinum mine at a cost of $5 million. A condition of mining the
platinum is a requirement to landscape the mining site at the end of its estimated life of ten years. The
present value of this cost at the date of the purchase was calculated at $3 million (in addition to the
purchase price of the mine of $5 million).
Also on 1 October 2008 Crosswire revalued its freehold land for the first time. The credit in the revaluation
reserve is the net amount of the revaluation after a transfer to deferred tax on the gain. The tax rate applicable to Crosswire for deferred tax is 20% per annum.
On 1 April 2009 Crosswire took out a finance lease for some new plant. The fair value of the plant was
$10 million. The lease agreement provided for an initial payment on 1 April 2009 of $2·4 million followed
by eight six-monthly payments of $1·2 million commencing 30 September 2009.
Plant disposed of during the year had a carrying amount of $500,000 and was sold for $1·2 million. The
remaining movement on the property, plant and equipment, after charging depreciation of $3 million, was
the cost of replacing plant.
(ii) From 1 October 2008 to 31 March 2009 a further $500,000 was spent completing the development
project at which date marketing and production started. The sales of the new product proved disappointing
and on 30 September 2009 the development costs were written down to $1 million via an impairment
charge.
(iii) During the year ended 30 September 2009, $4 million of the 10% convertible loan notes matured. The
loan note holders had the option of redemption at par in cash or to exchange them for equity shares on the
basis of 20 new shares for each $100 of loan notes. 75% of the loan-note holders chose the equity option.
Ignore any effect of this on the other equity reserve.
All the above items have been treated correctly according to International Financial Reporting Standards.
(iv) The finance costs are made up of:
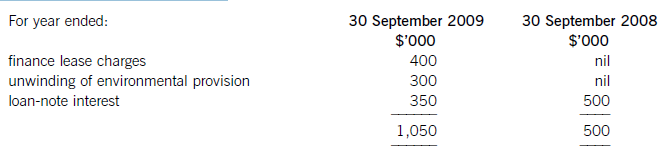
Required:
(i) Prepare a statement of the movements in the carrying amount of Crosswire’s non-current assets for the
year ended 30 September 2009; (9 marks)
(ii) Calculate the amounts that would appear under the headings of ‘cash flows from investing activities’
and ‘cash flows from financing activities’ in the statement of cash flows for Crosswire for the year ended
30 September 2009.
Note: Crosswire includes finance costs paid as a financing activity. (8 marks)
(b) A substantial shareholder has written to the directors of Crosswire expressing particular concern over the
deterioration of the company’s return on capital employed (ROCE)
Required:
Calculate Crosswire’s ROCE for the two years ended 30 September 2008 and 2009 and comment on the
apparent cause of its deterioration.
Note: ROCE should be taken as profit before interest on long-term borrowings and tax as a percentage of equity plus loan notes and finance lease obligations (at the year end). (8 marks)
相似考题
更多“(a) The following information relates to Crosswire a publicly listed company.Summarised statements of financial position as at:The following information is available:(i) During the year to 30 September 2009, Crosswire embarked on a replacement and expansi”相关问题
-
第1题:
11 The following information is available for Orset, a sole trader who does not keep full accounting records:
$
Inventory 1 July 2004 138,600
30 June 2005 149,100
Purchases for year ended 30 June 2005 716,100
Orset makes a standard gross profit of 30 per cent on sales.
Based on these figures, what is Orset’s sales figure for the year ended 30 June 2005?
A $2,352,000
B $1,038,000
C $917,280
D $1,008,000
正确答案:D
-
第2题:
5 An enterprise has made a material change to an accounting policy in preparing its current financial statements.
Which of the following disclosures are required by IAS 8 Accounting policies, changes in accounting estimates
and errors in these financial statements?
1 The reasons for the change.
2 The amount of the consequent adjustment in the current period and in comparative information for prior periods.
3 An estimate of the effect of the change on future periods, where possible.
A 1 and 2 only
B 1 and 3 only
C 2 and 3 only
D All three items
正确答案:A
-
第3题:
3 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Albreda Co, a limited liability company, and its subsidiaries. The
group mainly operates a chain of national restaurants and provides vending and other catering services to corporate
clients. All restaurants offer ‘eat-in’, ‘take-away’ and ‘home delivery’ services. The draft consolidated financial
statements for the year ended 30 September 2005 show revenue of $42·2 million (2004 – $41·8 million), profit
before taxation of $1·8 million (2004 – $2·2 million) and total assets of $30·7 million (2004 – $23·4 million).
The following issues arising during the final audit have been noted on a schedule of points for your attention:
(a) In September 2005 the management board announced plans to cease offering ‘home delivery’ services from the
end of the month. These sales amounted to $0·6 million for the year to 30 September 2005 (2004 – $0·8
million). A provision of $0·2 million has been made as at 30 September 2005 for the compensation of redundant
employees (mainly drivers). Delivery vehicles have been classified as non-current assets held for sale as at 30
September 2005 and measured at fair value less costs to sell, $0·8 million (carrying amount,
$0·5 million). (8 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Albreda Co for the year ended
30 September 2005.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:3 ALBREDA CO
(a) Cessation of ‘home delivery’ service
(i) Matters
■ $0·6 million represents 1·4% of reported revenue (prior year 1·9%) and is therefore material.
Tutorial note: However, it is clearly not of such significance that it should raise any doubts whatsoever regarding
the going concern assumption. (On the contrary, as revenue from this service has declined since last year.)
■ The home delivery service is not a component of Albreda and its cessation does not classify as a discontinued
operation (IFRS 5 ‘Non-current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations’).
? It is not a cash-generating unit because home delivery revenues are not independent of other revenues
generated by the restaurant kitchens.
? 1·4% of revenue is not a ‘major line of business’.
? Home delivery does not cover a separate geographical area (but many areas around the numerous
restaurants).
■ The redundancy provision of $0·2 million represents 11·1% of profit before tax (10% before allowing for the
provision) and is therefore material. However, it represents only 0·6% of total assets and is therefore immaterial
to the balance sheet.
■ As the provision is a liability it should have been tested primarily for understatement (completeness).
■ The delivery vehicles should be classified as held for sale if their carrying amount will be recovered principally
through a sale transaction rather than through continuing use. For this to be the case the following IFRS 5 criteria
must be met:
? the vehicles must be available for immediate sale in their present condition; and
? their sale must be highly probable.
Tutorial note: Highly probable = management commitment to a plan + initiation of plan to locate buyer(s) +
active marketing + completion expected in a year.
■ However, even if the classification as held for sale is appropriate the measurement basis is incorrect.
■ Non-current assets classified as held for sale should be carried at the lower of carrying amount and fair value less
costs to sell.
■ It is incorrect that the vehicles are being measured at fair value less costs to sell which is $0·3 million in excess
of the carrying amount. This amounts to a revaluation. Wherever the credit entry is (equity or income statement)
it should be reversed. $0·3 million represents just less than 1% of assets (16·7% of profit if the credit is to the
income statement).
■ Comparison of fair value less costs to sell against carrying amount should have been made on an item by item
basis (and not on their totals).
(ii) Audit evidence
■ Copy of board minute documenting management’s decision to cease home deliveries (and any press
releases/internal memoranda to staff).
■ An analysis of revenue (e.g. extracted from management accounts) showing the amount attributed to home delivery
sales.
■ Redundancy terms for drivers as set out in their contracts of employment.
■ A ‘proof in total’ for the reasonableness/completeness of the redundancy provision (e.g. number of drivers × sum
of years employed × payment per year of service).
■ A schedule of depreciated cost of delivery vehicles extracted from the non-current asset register.
■ Checking of fair values on a sample basis to second hand market prices (as published/advertised in used vehicle
guides).
■ After-date net sale proceeds from sale of vehicles and comparison of proceeds against estimated fair values.
■ Physical inspection of condition of unsold vehicles.
■ Separate disclosure of the held for sale assets on the face of the balance sheet or in the notes.
■ Assets classified as held for sale (and other disposals) shown in the reconciliation of carrying amount at the
beginning and end of the period.
■ Additional descriptions in the notes of:
? the non-current assets; and
? the facts and circumstances leading to the sale/disposal (i.e. cessation of home delivery service). -
第4题:
(b) You are an audit manager with specific responsibility for reviewing other information in documents containing
audited financial statements before your firm’s auditor’s report is signed. The financial statements of Hegas, a
privately-owned civil engineering company, show total assets of $120 million, revenue of $261 million, and profit
before tax of $9·2 million for the year ended 31 March 2005. Your review of the Annual Report has revealed
the following:
(i) The statement of changes in equity includes $4·5 million under a separate heading of ‘miscellaneous item’
which is described as ‘other difference not recognized in income’. There is no further reference to this
amount or ‘other difference’ elsewhere in the financial statements. However, the Management Report, which
is required by statute, is not audited. It discloses that ‘changes in shareholders’ equity not recognized in
income includes $4·5 million arising on the revaluation of investment properties’.
The notes to the financial statements state that the company has implemented IAS 40 ‘Investment Property’
for the first time in the year to 31 March 2005 and also that ‘the adoption of this standard did not have a
significant impact on Hegas’s financial position or its results of operations during 2005’.
(ii) The chairman’s statement asserts ‘Hegas has now achieved a position as one of the world’s largest
generators of hydro-electricity, with a dedicated commitment to accountable ethical professionalism’. Audit
working papers show that 14% of revenue was derived from hydro-electricity (2004: 12%). Publicly
available information shows that there are seven international suppliers of hydro-electricity in Africa alone,
which are all at least three times the size of Hegas in terms of both annual turnover and population supplied.
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of the above matters for the auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Hegas for the year ended 31 March 2005. (10 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Implications for the auditor’s report
(i) Management Report
■ $4·5 million represents 3·75% of total assets, 1·7% of revenue and 48·9% profit before tax. As this is material
by any criteria (exceeding all of 2% of total assets, 1/2% revenue and 5% PBT), the specific disclosure requirements
of IASs need to be met (IAS 1 ‘Presentation of Financial Statements’).
■ The Management Report discloses the amount and the reason for a material change in equity whereas the financial
statements do not show the reason for the change and suggest that it is immaterial. As the increase in equity
attributable to this adjustment is nearly half as much as that attributable to PBT there is a material inconsistency
between the Management Report and the audited financial statements.
■ Amendment to the Management Report is not required.
Tutorial note: Marks will be awarded for arguing, alternatively, that the Management Report disclosure needs to
be amended to clarify that the revaluation arises from the first time implementation.
■ Amendment to the financial statements is required because the disclosure is:
– incorrect – as, on first adoption of IAS 40, the fair value adjustment should be against the opening balance
of retained earnings; and
– inadequate – because it is being ‘supplemented’ by additional disclosure in a document which is not within
the scope of the audit of financial statements.
■ Whilst it is true that the adoption of IAS 40 did not have a significant impact on results of operations, Hegas’s
financial position has increased by nearly 4% in respect of the revaluation (to fair value) of just one asset category
(investment properties). As this is significant, the statement in the notes should be redrafted.
■ If the financial statements are not amended, the auditor’s report should be qualified ‘except for’ on grounds of
disagreement (non-compliance with IAS 40) as the matter is material but not pervasive. Additional disclosure
should also be given (e.g. that the ‘other difference’ is a fair value adjustment).
■ However, it is likely that when faced with the prospect of a qualified auditor’s report Hegas’s management will
rectify the financial statements so that an unmodified auditor’s report can be issued.
Tutorial note: Marks will be awarded for other relevant points e.g. citing IAS 8 ‘Accounting Policies, Changes in
Accounting Estimates and Errors’.
(ii) Chairman’s statement
Tutorial note: Hegas is privately-owned therefore IAS 14 ‘Segment Reporting’ does not apply and the proportion of
revenue attributable to hydro-electricity will not be required to be disclosed in the financial statements. However, credit
will be awarded for discussing the implications for the auditor’s report if it is regarded as a material inconsistency on
the assumption that segment revenue (or similar) is reported in the financial statements.
■ The assertion in the chairman’s statement, which does not fall within the scope of the audit of the financial
statements, claims two things, namely that the company:
(1) is ‘one of the world’s largest generators of hydro-electricity’; and
(2) has ‘a dedicated commitment to accountable ethical professionalism’.
■ To the extent that this information does not relate to matters disclosed in the financial statements it may give rise
to a material misstatement of fact. In particular, the first statement presents a misleading impression of the
company’s size. In misleading a user of the financial statements with this statement, the second statement is not
true (as it is not ethical or professional to mislead the reader and potentially undermine the credibility of the
financial statements).
■ The first statement is a material misstatement of fact because, for example:
– the company is privately-owned, and publicly-owned international/multi-nationals are larger;
– the company’s main activity is civil engineering not electricity generation (only 14% of revenue is derived from
HEP);
– as the company ranks at best eighth against African companies alone it ranks much lower globally.
■ Hegas should be asked to reconsider the wording of the chairman’s statement (i.e. removing these assertions) and
consult, as necessary, the company’s legal advisor.
■ If the statement is not changed there will be no grounds for qualification of the opinion on the audited financial
statements. The audit firm should therefore take legal advice on how the matter should be reported.
■ However, an emphasis of matter paragraph may be used to report on matters other than those affecting the audited
financial statements. For example, to explain the misstatement of fact if management refuses to make the
amendment.
Tutorial note: Marks will also be awarded for relevant comments about the chairman’s statement being perceived by
many readers to be subject to audit and therefore that the unfounded statement might undermine the credibility of the
financial statements. Shareholders tend to rely on the chairman’s statement, even though it is not regulated or audited,
because modern financial statements are so complex. -
第5题:
(b) Seymour offers health-related information services through a wholly-owned subsidiary, Aragon Co. Goodwill of
$1·8 million recognised on the purchase of Aragon in October 2004 is not amortised but included at cost in the
consolidated balance sheet. At 30 September 2006 Seymour’s investment in Aragon is shown at cost,
$4·5 million, in its separate financial statements.
Aragon’s draft financial statements for the year ended 30 September 2006 show a loss before taxation of
$0·6 million (2005 – $0·5 million loss) and total assets of $4·9 million (2005 – $5·7 million). The notes to
Aragon’s financial statements disclose that they have been prepared on a going concern basis that assumes that
Seymour will continue to provide financial support. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Seymour Co for the year ended
30 September 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
(b) Goodwill
(i) Matters
■ Cost of goodwill, $1·8 million, represents 3·4% consolidated total assets and is therefore material.
Tutorial note: Any assessments of materiality of goodwill against amounts in Aragon’s financial statements are
meaningless since goodwill only exists in the consolidated financial statements of Seymour.
■ It is correct that the goodwill is not being amortised (IFRS 3 Business Combinations). However, it should be tested
at least annually for impairment, by management.
■ Aragon has incurred losses amounting to $1·1 million since it was acquired (two years ago). The write-off of this
amount against goodwill in the consolidated financial statements would be material (being 61% cost of goodwill,
8·3% PBT and 2·1% total assets).
■ The cost of the investment ($4·5 million) in Seymour’s separate financial statements will also be material and
should be tested for impairment.
■ The fair value of net assets acquired was only $2·7 million ($4·5 million less $1·8 million). Therefore the fair
value less costs to sell of Aragon on other than a going concern basis will be less than the carrying amount of the
investment (i.e. the investment is impaired by at least the amount of goodwill recognised on acquisition).
■ In assessing recoverable amount, value in use (rather than fair value less costs to sell) is only relevant if the going
concern assumption is appropriate for Aragon.
■ Supporting Aragon financially may result in Seymour being exposed to actual and/or contingent liabilities that
should be provided for/disclosed in Seymour’s financial statements in accordance with IAS 37 Provisions,
Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ Carrying values of cost of investment and goodwill arising on acquisition to prior year audit working papers and
financial statements.
■ A copy of Aragon’s draft financial statements for the year ended 30 September 2006 showing loss for year.
■ Management’s impairment test of Seymour’s investment in Aragon and of the goodwill arising on consolidation at
30 September 2006. That is a comparison of the present value of the future cash flows expected to be generated
by Aragon (a cash-generating unit) compared with the cost of the investment (in Seymour’s separate financial
statements).
■ Results of any impairment tests on Aragon’s assets extracted from Aragon’s working paper files.
■ Analytical procedures on future cash flows to confirm their reasonableness (e.g. by comparison with cash flows for
the last two years).
■ Bank report for audit purposes for any guarantees supporting Aragon’s loan facilities.
■ A copy of Seymour’s ‘comfort letter’ confirming continuing financial support of Aragon for the foreseeable future. -
第6题:
On 1 April 2009 Pandar purchased 80% of the equity shares in Salva. The acquisition was through a share exchange of three shares in Pandar for every five shares in Salva. The market prices of Pandar’s and Salva’s shares at 1 April
2009 were $6 per share and $3.20 respectively.
On the same date Pandar acquired 40% of the equity shares in Ambra paying $2 per share.
The summarised income statements for the three companies for the year ended 30 September 2009 are:
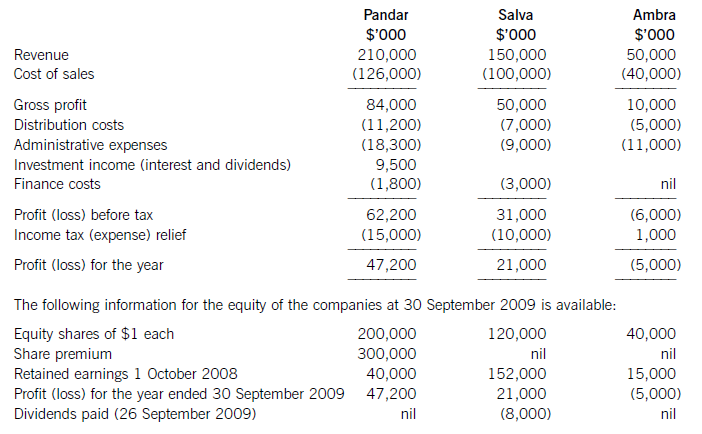
The following information is relevant:
(i) The fair values of the net assets of Salva at the date of acquisition were equal to their carrying amounts with the exception of an item of plant which had a carrying amount of $12 million and a fair value of $17 million. This plant had a remaining life of five years (straight-line depreciation) at the date of acquisition of Salva. All depreciation is charged to cost of sales.
In addition Salva owns the registration of a popular internet domain name. The registration, which had a
negligible cost, has a five year remaining life (at the date of acquisition); however, it is renewable indefinitely at a nominal cost. At the date of acquisition the domain name was valued by a specialist company at $20 million.
The fair values of the plant and the domain name have not been reflected in Salva’s financial statements.
No fair value adjustments were required on the acquisition of the investment in Ambra.
(ii) Immediately after its acquisition of Salva, Pandar invested $50 million in an 8% loan note from Salva. All interest accruing to 30 September 2009 had been accounted for by both companies. Salva also has other loans in issue at 30 September 2009.
(iii) Pandar has credited the whole of the dividend it received from Salva to investment income.
(iv) After the acquisition, Pandar sold goods to Salva for $15 million on which Pandar made a gross profit of 20%. Salva had one third of these goods still in its inventory at 30 September 2009. There are no intra-group current account balances at 30 September 2009.
(v) The non-controlling interest in Salva is to be valued at its (full) fair value at the date of acquisition. For this
purpose Salva’s share price at that date can be taken to be indicative of the fair value of the shareholding of the non-controlling interest.
(vi) The goodwill of Salva has not suffered any impairment; however, due to its losses, the value of Pandar’s
investment in Ambra has been impaired by $3 million at 30 September 2009.
(vii) All items in the above income statements are deemed to accrue evenly over the year unless otherwise indicated.
Required:
(a) (i) Calculate the goodwill arising on the acquisition of Salva at 1 April 2009; (6 marks)
(ii) Calculate the carrying amount of the investment in Ambra to be included within the consolidated
statement of financial position as at 30 September 2009. (3 marks)
(b) Prepare the consolidated income statement for the Pandar Group for the year ended 30 September 2009.(16 marks)
正确答案:
-
第7题:
(a) An assistant of yours has been criticised over a piece of assessed work that he produced for his study course for giving the definition of a non-current asset as ‘a physical asset of substantial cost, owned by the company, which will last longer than one year’.
Required:
Provide an explanation to your assistant of the weaknesses in his definition of non-current assets when
compared to the International Accounting Standards Board’s (IASB) view of assets. (4 marks)
(b) The same assistant has encountered the following matters during the preparation of the draft financial statements of Darby for the year ending 30 September 2009. He has given an explanation of his treatment of them.
(i) Darby spent $200,000 sending its staff on training courses during the year. This has already led to an
improvement in the company’s efficiency and resulted in cost savings. The organiser of the course has stated that the benefits from the training should last for a minimum of four years. The assistant has therefore treated the cost of the training as an intangible asset and charged six months’ amortisation based on the average date during the year on which the training courses were completed. (3 marks)
(ii) During the year the company started research work with a view to the eventual development of a new
processor chip. By 30 September 2009 it had spent $1·6 million on this project. Darby has a past history
of being particularly successful in bringing similar projects to a profitable conclusion. As a consequence the
assistant has treated the expenditure to date on this project as an asset in the statement of financial position.
Darby was also commissioned by a customer to research and, if feasible, produce a computer system to
install in motor vehicles that can automatically stop the vehicle if it is about to be involved in a collision. At
30 September 2009, Darby had spent $2·4 million on this project, but at this date it was uncertain as to
whether the project would be successful. As a consequence the assistant has treated the $2·4 million as an
expense in the income statement. (4 marks)
(iii) Darby signed a contract (for an initial three years) in August 2009 with a company called Media Today to
install a satellite dish and cabling system to a newly built group of residential apartments. Media Today will
provide telephone and television services to the residents of the apartments via the satellite system and pay
Darby $50,000 per annum commencing in December 2009. Work on the installation commenced on
1 September 2009 and the expenditure to 30 September 2009 was $58,000. The installation is expected
to be completed by 31 October 2009. Previous experience with similar contracts indicates that Darby will
make a total profit of $40,000 over the three years on this initial contract. The assistant correctly recorded
the costs to 30 September 2009 of $58,000 as a non-current asset, but then wrote this amount down to
$40,000 (the expected total profit) because he believed the asset to be impaired.
The contract is not a finance lease. Ignore discounting. (4 marks)
Required:
For each of the above items (i) to (iii) comment on the assistant’s treatment of them in the financial
statements for the year ended 30 September 2009 and advise him how they should be treated under
International Financial Reporting Standards.
Note: the mark allocation is shown against each of the three items above.
正确答案:
(a)Therearefourelementstotheassistant’sdefinitionofanon-currentassetandheissubstantiallyincorrectinrespectofallofthem.Thetermnon-currentassetswillnormallyincludeintangibleassetsandcertaininvestments;theuseoftheterm‘physicalasset’wouldbespecifictotangibleassetsonly.Whilstitisusuallythecasethatnon-currentassetsareofrelativelyhighvaluethisisnotadefiningaspect.Awastepaperbinmayexhibitthecharacteristicsofanon-currentasset,butonthegroundsofmaterialityitisunlikelytobetreatedassuch.Furthermorethepastcostofanassetmaybeirrelevant;nomatterhowmuchanassethascost,itistheexpectationoffutureeconomicbenefitsflowingfromaresource(normallyintheform.offuturecashinflows)thatdefinesanassetaccordingtotheIASB’sFrameworkforthepreparationandpresentationoffinancialstatements.Theconceptofownershipisnolongeracriticalaspectofthedefinitionofanasset.Itisprobablythecasethatmostnoncurrentassetsinanentity’sstatementoffinancialpositionareownedbytheentity;however,itistheabilityto‘control’assets(includingpreventingothersfromhavingaccesstothem)thatisnowadefiningfeature.Forexample:thisisanimportantcharacteristicintreatingafinanceleaseasanassetofthelesseeratherthanthelessor.Itisalsotruethatmostnon-currentassetswillbeusedbyanentityformorethanoneyearandapartofthedefinitionofproperty,plantandequipmentinIAS16Property,plantandequipmentreferstoanexpectationofuseinmorethanoneperiod,butthisisnotnecessarilyalwaysthecase.Itmaybethatanon-currentassetisacquiredwhichprovesunsuitablefortheentity’sintendeduseorisdamagedinanaccident.Inthesecircumstancesassetsmaynothavebeenusedforlongerthanayear,butneverthelesstheywerereportedasnon-currentsduringthetimetheywereinuse.Anon-currentassetmaybewithinayearoftheendofitsusefullifebut(unlessasaleagreementhasbeenreachedunderIFRS5Non-currentassetsheldforsaleanddiscontinuedoperations)wouldstillbereportedasanon-currentassetifitwasstillgivingeconomicbenefits.Anotherdefiningaspectofnon-currentassetsistheirintendedusei.e.heldforcontinuinguseintheproduction,supplyofgoodsorservices,forrentaltoothersorforadministrativepurposes.(b)(i)TheexpenditureonthetrainingcoursesmayexhibitthecharacteristicsofanassetinthattheyhaveandwillcontinuetobringfutureeconomicbenefitsbywayofincreasedefficiencyandcostsavingstoDarby.However,theexpenditurecannotberecognisedasanassetonthestatementoffinancialpositionandmustbechargedasanexpenseasthecostisincurred.Themainreasonforthislieswiththeissueof’control’;itisDarby’semployeesthathavethe‘skills’providedbythecourses,buttheemployeescanleavethecompanyandtaketheirskillswiththemor,throughaccidentorinjury,maybedeprivedofthoseskills.AlsothecapitalisationofstafftrainingcostsisspecificallyprohibitedunderInternationalFinancialReportingStandards(specificallyIAS38Intangibleassets).(ii)Thequestionspecificallystatesthatthecostsincurredtodateonthedevelopmentofthenewprocessorchipareresearchcosts.IAS38statesthatresearchcostsmustbeexpensed.Thisismainlybecauseresearchistherelativelyearlystageofanewprojectandanyfuturebenefitsaresofarinthefuturethattheycannotbeconsideredtomeetthedefinitionofanasset(probablefutureeconomicbenefits),despitethegoodrecordofsuccessinthepastwithsimilarprojects.Althoughtheworkontheautomaticvehiclebrakingsystemisstillattheresearchstage,thisisdifferentinnaturefromthepreviousexampleastheworkhasbeencommissionedbyacustomer,Assuch,fromtheperspectiveofDarby,itisworkinprogress(acurrentasset)andshouldnotbewrittenoffasanexpense.Anoteofcautionshouldbeaddedhereinthatthequestionsaysthatthesuccessoftheprojectisuncertainwhichpresumablymeansitmaynotbecompleted.ThisdoesnotmeanthatDarbywillnotreceivepaymentfortheworkithascarriedout,butitshouldbecheckedtothecontracttoensurethattheamountithasspenttodate($2·4million)willberecoverable.Intheeventthatsay,forexample,thecontractstatedthatonly$2millionwouldbeallowedforresearchcosts,thiswouldplacealimitonhowmuchDarbycouldtreatasworkinprogress.Ifthiswerethecasethen,forthisexample,Darbywouldhavetoexpense$400,000andtreatonly$2millionasworkinprogress.(iii)Thequestionsuggeststhecorrecttreatmentforthiskindofcontractistotreatthecostsoftheinstallationasanon-currentassetand(presumably)depreciateitoveritsexpectedlifeof(atleast)threeyearsfromwhenitbecomesavailableforuse.Inthiscasetheassetwillnotcomeintouseuntilthenextfinancialyear/reportingperiodandnodepreciationneedstobeprovidedat30September2009.Thecapitalisedcoststodateof$58,000shouldonlybewrittendownifthereisevidencethattheassethasbecomeimpaired.Impairmentoccurswheretherecoverableamountofanassetislessthanitscarryingamount.Theassistantappearstobelievethattherecoverableamountisthefutureprofit,whereas(inthiscase)itisthefuture(net)cashinflows.Thusanyimpairmenttestat30September2009shouldcomparethecarryingamountof$58,000withtheexpectednetcashflowfromthesystemof$98,000($50,000perannumforthreeyearslessfuturecashoutflowstocompletiontheinstallationof$52,000(seenotebelow)).Asthefuturenetcashflowsareinexcessofthecarryingamount,theassetisnotimpairedanditshouldnotbewrittendownbutshownasanon-currentasset(underconstruction)atcostof$58,000.Note:asthecontractisexpectedtomakeaprofitof$40,000onincomeof$150,000,thetotalcostsmustbe$110,000,withcoststodateat$58,000thisleavescompletioncostsof$52,000. -
第8题:
You are an audit manager at Rockwell & Co, a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants. You are responsible for the audit of the Hopper Group, a listed audit client which supplies ingredients to the food and beverage industry worldwide.
The audit work for the year ended 30 June 2015 is nearly complete, and you are reviewing the draft audit report which has been prepared by the audit senior. During the year the Hopper Group purchased a new subsidiary company, Seurat Sweeteners Co, which has expertise in the research and design of sugar alternatives. The draft financial statements of the Hopper Group for the year ended 30 June 2015 recognise profit before tax of $495 million (2014 – $462 million) and total assets of $4,617 million (2014: $4,751 million). An extract from the draft audit report is shown below:
Basis of modified opinion (extract)
In their calculation of goodwill on the acquisition of the new subsidiary, the directors have failed to recognise consideration which is contingent upon meeting certain development targets. The directors believe that it is unlikely that these targets will be met by the subsidiary company and, therefore, have not recorded the contingent consideration in the cost of the acquisition. They have disclosed this contingent liability fully in the notes to the financial statements. We do not feel that the directors’ treatment of the contingent consideration is correct and, therefore, do not believe that the criteria of the relevant standard have been met. If this is the case, it would be appropriate to adjust the goodwill balance in the statement of financial position.
We believe that any required adjustment may materially affect the goodwill balance in the statement of financial position. Therefore, in our opinion, the financial statements do not give a true and fair view of the financial position of the Hopper Group and of the Hopper Group’s financial performance and cash flows for the year then ended in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards.
Emphasis of Matter Paragraph
We draw attention to the note to the financial statements which describes the uncertainty relating to the contingent consideration described above. The note provides further information necessary to understand the potential implications of the contingency.
Required:
(a) Critically appraise the draft audit report of the Hopper Group for the year ended 30 June 2015, prepared by the audit senior.
Note: You are NOT required to re-draft the extracts from the audit report. (10 marks)
(b) The audit of the new subsidiary, Seurat Sweeteners Co, was performed by a different firm of auditors, Fish Associates. During your review of the communication from Fish Associates, you note that they were unable to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence with regard to the breakdown of research expenses. The total of research costs expensed by Seurat Sweeteners Co during the year was $1·2 million. Fish Associates has issued a qualified audit opinion on the financial statements of Seurat Sweeteners Co due to this inability to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence.
Required:
Comment on the actions which Rockwell & Co should take as the auditor of the Hopper Group, and the implications for the auditor’s report on the Hopper Group financial statements. (6 marks)
(c) Discuss the quality control procedures which should be carried out by Rockwell & Co prior to the audit report on the Hopper Group being issued. (4 marks)
正确答案:(a) Critical appraisal of the draft audit report
Type of opinion
When an auditor issues an opinion expressing that the financial statements ‘do not give a true and fair view’, this represents an adverse opinion. The paragraph explaining the modification should, therefore, be titled ‘Basis of Adverse Opinion’ rather than simply ‘Basis of Modified Opinion’.
An adverse opinion means that the auditor considers the misstatement to be material and pervasive to the financial statements of the Hopper Group. According to ISA 705 Modifications to Opinions in the Independent Auditor’s Report, pervasive matters are those which affect a substantial proportion of the financial statements or fundamentally affect the users’ understanding of the financial statements. It is unlikely that the failure to recognise contingent consideration is pervasive; the main effect would be to understate goodwill and liabilities. This would not be considered a substantial proportion of the financial statements, neither would it be fundamental to understanding the Hopper Group’s performance and position.
However, there is also some uncertainty as to whether the matter is even material. If the matter is determined to be material but not pervasive, then a qualified opinion would be appropriate on the basis of a material misstatement. If the matter is not material, then no modification would be necessary to the audit opinion.
Wording of opinion/report
The auditor’s reference to ‘the acquisition of the new subsidiary’ is too vague; the Hopper Group may have purchased a number of subsidiaries which this phrase could relate to. It is important that the auditor provides adequate description of the event and in these circumstances it would be appropriate to name the subsidiary referred to.
The auditor has not quantified the amount of the contingent element of the consideration. For the users to understand the potential implications of any necessary adjustments, they need to know how much the contingent consideration will be if it becomes payable. It is a requirement of ISA 705 that the auditor quantifies the financial effects of any misstatements, unless it is impracticable to do so.
In addition to the above point, the auditor should provide more description of the financial effects of the misstatement, including full quantification of the effect of the required adjustment to the assets, liabilities, incomes, revenues and equity of the Hopper Group.
The auditor should identify the note to the financial statements relevant to the contingent liability disclosure rather than just stating ‘in the note’. This will improve the understandability and usefulness of the contents of the audit report.
The use of the term ‘we do not feel that the treatment is correct’ is too vague and not professional. While there may be some interpretation necessary when trying to apply financial reporting standards to unique circumstances, the expression used is ambiguous and may be interpreted as some form. of disclaimer by the auditor with regard to the correct accounting treatment. The auditor should clearly explain how the treatment applied in the financial statements has departed from the requirements of the relevant standard.
Tutorial note: As an illustration to the above point, an appropriate wording would be: ‘Management has not recognised the acquisition-date fair value of contingent consideration as part of the consideration transferred in exchange for the acquiree, which constitutes a departure from International Financial Reporting Standards.’
The ambiguity is compounded by the use of the phrase ‘if this is the case, it would be appropriate to adjust the goodwill’. This once again suggests that the correct treatment is uncertain and perhaps open to interpretation.
If the auditor wishes to refer to a specific accounting standard they should refer to its full title. Therefore instead of referring to ‘the relevant standard’ they should refer to International Financial Reporting Standard 3 Business Combinations.
The opinion paragraph requires an appropriate heading. In this case the auditors have issued an adverse opinion and the paragraph should be headed ‘Adverse Opinion’.
As with the basis paragraph, the opinion paragraph lacks authority; suggesting that the required adjustments ‘may’ materially affect the financial statements implies that there is a degree of uncertainty. This is not the case; the amount of the contingent consideration will be disclosed in the relevant purchase agreement, so the auditor should be able to determine whether the required adjustments are material or not. Regardless, the sentence discussing whether the balance is material or not is not required in the audit report as to warrant inclusion in the report the matter must be considered material. The disclosure of the nature and financial effect of the misstatement in the basis paragraph is sufficient.
Finally, the emphasis of matter paragraph should not be included in the audit report. An emphasis of matter paragraph is only used to draw attention to an uncertainty/matter of fundamental importance which is correctly accounted for and disclosed in the financial statements. An emphasis of matter is not required in this case for the following reasons:
– Emphasis of matter is only required to highlight matters which the auditor believes are fundamental to the users’ understanding of the business. An example may be where a contingent liability exists which is so significant it could lead to the closure of the reporting entity. That is not the case with the Hopper Group; the contingent liability does not appear to be fundamental.
– Emphasis of matter is only used for matters where the auditor has obtained sufficient appropriate evidence that the matter is not materially misstated in the financial statements. If the financial statements are materially misstated, in this regard the matter would be fully disclosed by the auditor in the basis of qualified/adverse opinion paragraph and no emphasis of matter is necessary.
(b) Communication from the component auditor
The qualified opinion due to insufficient evidence may be a significant matter for the Hopper Group audit. While the possible adjustments relating to the current year may not be material to the Hopper Group, the inability to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence with regard to a material matter in Seurat Sweeteners Co’s financial statements may indicate a control deficiency which the auditor was not aware of at the planning stage and it could indicate potential problems with regard to the integrity of management, which could also indicate a potential fraud. It could also indicate an unwillingness of management to provide information, which could create problems for future audits, particularly if research and development costs increase in future years. If the group auditor suspects that any of these possibilities are true, they may need to reconsider their risk assessment and whether the audit procedures performed are still appropriate.
If the detail provided in the communication from the component auditor is insufficient, the group auditor should first discuss the matter with the component auditor to see whether any further information can be provided. The group auditor can request further working papers from the component auditor if this is necessary. However, if Seurat Sweeteners has not been able to provide sufficient appropriate evidence, it is unlikely that this will be effective.
If the discussions with the component auditor do not provide satisfactory responses to evaluate the potential impact on the Hopper Group, the group auditor may need to communicate with either the management of Seurat Sweeteners or the Hopper Group to obtain necessary clarification with regard to the matter.
Following these procedures, the group auditor needs to determine whether they have sufficient appropriate evidence to draw reasonable conclusions on the Hopper Group’s financial statements. If they believe the lack of information presents a risk of material misstatement in the group financial statements, they can request that further audit procedures be performed, either by the component auditor or by themselves.
Ultimately the group engagement partner has to evaluate the effect of the inability to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence on the audit opinion of the Hopper Group. The matter relates to research expenses totalling $1·2 million, which represents 0·2% of the profit for the year and 0·03% of the total assets of the Hopper Group. It is therefore not material to the Hopper Group’s financial statements. For this reason no modification to the audit report of the Hopper Group would be required as this does not represent a lack of sufficient appropriate evidence with regard to a matter which is material to the Group financial statements.
Although this may not have an impact on the Hopper Group audit opinion, this may be something the group auditor wishes to bring to the attention of those charged with governance. This would be particularly likely if the group auditor believed that this could indicate some form. of fraud in Seurat Sweeteners Co, a serious deficiency in financial reporting controls or if this could create problems for accepting future audits due to management’s unwillingness to provide access to accounting records.
(c) Quality control procedures prior to issuing the audit report
ISA 220 Quality Control for an Audit of Financial Statements and ISQC 1 Quality Control for Firms that Perform. Audits and Reviews of Historical Financial Information, and Other Assurance and Related Services Agreements require that an engagement quality control reviewer shall be appointed for audits of financial statements of listed entities. The audit engagement partner then discusses significant matters arising during the audit engagement with the engagement quality control reviewer.
The engagement quality control reviewer and the engagement partner should discuss the failure to recognise the contingent consideration and its impact on the auditor’s report. The engagement quality control reviewer must review the financial statements and the proposed auditor’s report, in particular focusing on the conclusions reached in formulating the auditor’s report and consideration of whether the proposed auditor’s opinion is appropriate. The audit documentation relating to the acquisition of Seurat Sweeteners Co will be carefully reviewed, and the reviewer is likely to consider whether procedures performed in relation to these balances were appropriate.
Given the listed status of the Hopper Group, any modification to the auditor’s report will be scrutinised, and the firm must be sure of any decision to modify the report, and the type of modification made. Once the engagement quality control reviewer has considered the necessity of a modification, they should consider whether a qualified or an adverse opinion is appropriate in the circumstances. This is an important issue, given that it requires judgement as to whether the matters would be material or pervasive to the financial statements.
The engagement quality control reviewer should ensure that there is adequate documentation regarding the judgements used in forming the final audit opinion, and that all necessary matters have been brought to the attention of those charged with governance.
The auditor’s report must not be signed and dated until the completion of the engagement quality control review.
Tutorial note: In the case of the Hopper Group’s audit, the lack of evidence in respect of research costs is unlikely to be discussed unless the audit engagement partner believes that the matter could be significant, for example, if they suspected the lack of evidence is being used to cover up a financial statements fraud.
-
第9题:
Raymond and Howell proposed job cuts following a two-year decline in sales ()a.figures
b.actions
c.employers
d.information答案:A解析: -
第10题:
单选题Which of the following commands should be used to obtain information about the software packages available on the installation media?()Alsattr
Binutoc
Cinstallp
Dlsresource
正确答案: B解析: 暂无解析 -
第11题:
问答题You are required to write an email of no fewer than 80 words to your manager, according to the following information given in Chinese. You should include all the points listed in the following table. Now write the message on the Answer Sheet.正确答案:
Producing Situations
Mr. Liu,
I would like to give you, the production manager, a brief report on producing situations in our production department. Generally, the producing runs well with 500,000 ton as its daily output. And the coal that is desperately needed in producing lines has already been delivered and arrived this morning. What’s more, the HAD company requires to renew the contact for a year in a letter and the renewal has already gone through the formalities and come into effect.
Best Wishes!
Yours,
Li Chengyuan解析: 暂无解析 -
第12题:
单选题The passage is primarily concerned with which of the following?ADescribing the life cycle of the Plasmodium protozoan as it relates to the disease malaria
BComparing and contrasting the life cycles of the six variants of the Plasmodium protozoan known to cause malaria
CAddressing the public health implications of the life cycle of the Plasmodium parasite
DProviding information on how a person can avoid infection with malaria
EDescribing the life cycle of the Anopheles mosquito as it relates to the transmission of the Plasmodium protozoan to humans
正确答案: B解析:
主旨题。文章主要在介绍与疟疾原生动物疟原虫的生命周期,故应选A项。 -
第13题:
(b) Discuss the relative costs to the preparer and benefits to the users of financial statements of increased
disclosure of information in financial statements. (14 marks)
Quality of discussion and reasoning. (2 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Increased information disclosure benefits users by reducing the likelihood that they will misallocate their capital. This is
obviously a direct benefit to individual users of corporate reports. The disclosure reduces the risk of misallocation of capital
by enabling users to improve their assessments of a company’s prospects. This creates three important results.
(i) Users use information disclosed to increase their investment returns and by definition support the most profitable
companies which are likely to be those that contribute most to economic growth. Thus, an important benefit of
information disclosure is that it improves the effectiveness of the investment process.
(ii) The second result lies in the effect on the liquidity of the capital markets. A more liquid market assists the effective
allocation of capital by allowing users to reallocate their capital quickly. The degree of information asymmetry between
the buyer and seller and the degree of uncertainty of the buyer and the seller will affect the liquidity of the market as
lower asymmetry and less uncertainty will increase the number of transactions and make the market more liquid.
Disclosure will affect uncertainty and information asymmetry.
(iii) Information disclosure helps users understand the risk of a prospective investment. Without any information, the user
has no way of assessing a company’s prospects. Information disclosure helps investors predict a company’s prospects.
Getting a better understanding of the true risk could lower the price of capital for the company. It is difficult to prove
however that the average cost of capital is lowered by information disclosure, even though it is logically and practically
impossible to assess a company’s risk without relevant information. Lower capital costs promote investment, which can
stimulate productivity and economic growth.
However although increased information can benefit users, there are problems of understandability and information overload.
Information disclosure provides a degree of protection to users. The benefit is fairness to users and is part of corporate
accountability to society as a whole.
The main costs to the preparer of financial statements are as follows:
(i) the cost of developing and disseminating information,
(ii) the cost of possible litigation attributable to information disclosure,
(iii) the cost of competitive disadvantage attributable to disclosure.
The costs of developing and disseminating the information include those of gathering, creating and auditing the information.
Additional costs to the preparers include training costs, changes to systems (for example on moving to IFRS), and the more
complex and the greater the information provided, the more it will cost the company.
Although litigation costs are known to arise from information disclosure, it does not follow that all information disclosure leads
to litigation costs. Cases can arise from insufficient disclosure and misleading disclosure. Only the latter is normally prompted
by the presentation of information disclosure. Fuller disclosure could lead to lower costs of litigation as the stock market would
have more realistic expectations of the company’s prospects and the discrepancy between the valuation implicit in the market
price and the valuation based on a company’s financial statements would be lower. However, litigation costs do not
necessarily increase with the extent of the disclosure. Increased disclosure could reduce litigation costs.
Disclosure could weaken a company’s ability to generate future cash flows by aiding its competitors. The effect of disclosure
on competitiveness involves benefits as well as costs. Competitive disadvantage could be created if disclosure is made relating
to strategies, plans, (for example, planned product development, new market targeting) or information about operations (for
example, production-cost figures). There is a significant difference between the purpose of disclosure to users and
competitors. The purpose of disclosure to users is to help them to estimate the amount, timing, and certainty of future cash
flows. Competitors are not trying to predict a company’s future cash flows, and information of use in that context is not
necessarily of use in obtaining competitive advantage. Overlap between information designed to meet users’ needs and
information designed to further the purposes of a competitor is often coincidental. Every company that could suffer competitive
disadvantage from disclosure could gain competitive advantage from comparable disclosure by competitors. Published figures
are often aggregated with little use to competitors.
Companies bargain with suppliers and with customers, and information disclosure could give those parties an advantage in
negotiations. In such cases, the advantage would be a cost for the disclosing entity. However, the cost would be offset
whenever information disclosure was presented by both parties, each would receive an advantage and a disadvantage.
There are other criteria to consider such as whether the information to be disclosed is about the company. This is both a
benefit and a cost criterion. Users of corporate reports need company-specific data, and it is typically more costly to obtain
and present information about matters external to the company. Additionally, consideration must be given as to whether the
company is the best source for the information. It could be inefficient for a company to obtain or develop data that other, more
expert parties could develop and present or do develop at present.
There are many benefits to information disclosure and users have unmet information needs. It cannot be known with any
certainty what the optimal disclosure level is for companies. Some companies through voluntary disclosure may have
achieved their optimal level. There are no quantitative measures of how levels of disclosure stand with respect to optimal
levels. Standard setters have to make such estimates as best they can, guided by prudence, and by what evidence of benefits
and costs they can obtain. -
第14题:
(b) Using the information contained in Appendix 1.1, discuss the financial performance of HLP and MAS,
incorporating details of the following in your discussion:
(i) Overall client fees (total and per consultation)
(ii) Advisory protection scheme consultation ‘utilisation levels’ for both property and commercial clients
(iii) Cost/expense levels. (10 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) As far as annual agreements relating to property work are concerned, HLP had a take up rate of 82·5% whereas MAS
had a take up rate of only 50%. Therefore, HLP has ‘lost out’ to competitor MAS in relative financial terms as regards
the ‘take-up’ of consultations relating to property work. This is because both HLP and MAS received an annual fee from
each property client irrespective of the number of consultations given. MAS should therefore have had a better profit
margin from this area of business than HLP. However, the extent to which HLP has ‘lost out’ cannot be quantified since
we would need to know the variable costs per consultation and this detail is not available. What we do know is that
HLP earned actual revenue per effective consultation amounting to £90·90 whereas the budgeted revenue per
consultation amounted to £100. MAS earned £120 per effective consultation.
The same picture emerges from annual agreements relating to commercial work. HLP had a budgeted take up rate of
50%, however the actual take up rate during the period was 90%. MAS had an actual take up rate of 50%. The actual
revenue per effective consultation earned by HLP amounted to £167 whereas the budgeted revenue per consultation
amounted to £300. MAS earned £250 per effective consultation.
There could possibly be an upside to this situation for HLP in that it might be the case that the uptake of 90% of
consultations without further charge by clients holding annual agreements in respect of commercial work might be
indicative of a high level of customer satisfaction. It could on the other hand be indicative of a mindset which says ‘I
have already paid for these consultations therefore I am going to request them’.
(iii) Budgeted and actual salaries in HLP were £50,000 per annum, per advisor. Two additional advisors were employed
during the year in order to provide consultations in respect of commercial work. MAS paid a salary of £60,000 to each
advisor which is 20% higher than the salary of £50,000 paid to each advisor by HLP. Perhaps this is indicative that
the advisors employed by MAS are more experienced and/or better qualified than those employed by HLP.
HLP paid indemnity insurance of £250,000 which is £150,000 (150%) more than the amount of £100,000 paid by
MAS. This excess cost may well have arisen as a consequence of successful claims against HLP for negligence in
undertaking commercial work. It would be interesting to know whether HLP had been the subject of any successful
claims for negligent work during recent years as premiums invariably reflect the claims history of a business. Rather
worrying is the fact that HLP was subject to three such claims during the year ended 31 May 2007.
Significant subcontract costs were incurred by HLP during the year probably in an attempt to satisfy demand and retain
the goodwill of its clients. HLP incurred subcontract costs in respect of commercial properties which totalled £144,000.
These consultations earned revenue amounting to (320 x £150) = £48,000, hence a loss of £96,000 was incurred
in this area of the business.
HLP also paid £300,000 for 600 subcontract consultations in respect of litigation work. These consultations earned
revenue amounting to (600 x £250) = £150,000, hence a loss of £150,000 was incurred in this area of the business.
In contrast, MAS paid £7,000 for 20 subcontract consultations in respect of commercial work and an identical amount
for 20 subcontract consultations in respect of litigation work. These consultations earned revenue amounting to
20 x (£150 + £200) =£7,000. Therefore, a loss of only £7,000 was incurred in respect of subcontract consultations
by MAS.
Other operating expenses were budgeted at 53·0% of sales revenue. The actual level incurred was 40·7% of sales
revenue. The fixed/variable split of such costs is not given but it may well be the case that the fall in this percentage is
due to good cost control by HLP. However, it might simply be the case that the original budget was flawed. Competitor
MAS would appear to have a slightly superior cost structure to that of HLP since its other operating expenses amounted
to 38·4% of sales revenue. Further information is required in order to draw firmer conclusions regarding cost control
within both businesses. -
第15题:
(c) During the year Albreda paid $0·1 million (2004 – $0·3 million) in fines and penalties relating to breaches of
health and safety regulations. These amounts have not been separately disclosed but included in cost of sales.
(5 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Albreda Co for the year ended
30 September 2005.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
(c) Fines and penalties
(i) Matters
■ $0·1 million represents 5·6% of profit before tax and is therefore material. However, profit has fallen, and
compared with prior year profit it is less than 5%. So ‘borderline’ material in quantitative terms.
■ Prior year amount was three times as much and represented 13·6% of profit before tax.
■ Even though the payments may be regarded as material ‘by nature’ separate disclosure may not be necessary if,
for example, there are no external shareholders.
■ Treatment (inclusion in cost of sales) should be consistent with prior year (‘The Framework’/IAS 1 ‘Presentation of
Financial Statements’).
■ The reason for the fall in expense. For example, whether due to an improvement in meeting health and safety
regulations and/or incomplete recording of liabilities (understatement).
■ The reason(s) for the breaches. For example, Albreda may have had difficulty implementing new guidelines in
response to stricter regulations.
■ Whether expenditure has been adjusted for in the income tax computation (as disallowed for tax purposes).
■ Management’s attitude to health and safety issues (e.g. if it regards breaches as an acceptable operational practice
or cheaper than compliance).
■ Any references to health and safety issues in other information in documents containing audited financial
statements that might conflict with Albreda incurring these costs.
■ Any cost savings resulting from breaches of health and safety regulations would result in Albreda possessing
proceeds of its own crime which may be a money laundering offence.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ A schedule of amounts paid totalling $0·1 million with larger amounts being agreed to the cash book/bank
statements.
■ Review/comparison of current year schedule against prior year for any apparent omissions.
■ Review of after-date cash book payments and correspondence with relevant health and safety regulators (e.g. local
authorities) for liabilities incurred before 30 September 2005.
■ Notes in the prior year financial statements confirming consistency, or otherwise, of the lack of separate disclosure.
■ A ‘signed off’ review of ‘other information’ (i.e. directors’ report, chairman’s statement, etc).
■ Written management representation that there are no fines/penalties other than those which have been reflected in
the financial statements. -
第16题:
3 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Seymour Co. The company offers information, proprietary foods and
medical innovations designed to improve the quality of life. (Proprietary foods are marketed under and protected by
registered names.) The draft consolidated financial statements for the year ended 30 September 2006 show revenue
of $74·4 million (2005 – $69·2 million), profit before taxation of $13·2 million (2005 – $15·8 million) and total
assets of $53·3 million (2005 – $40·5 million).
The following issues arising during the final audit have been noted on a schedule of points for your attention:
(a) In 2001, Seymour had been awarded a 20-year patent on a new drug, Tournose, that was also approved for
food use. The drug had been developed at a cost of $4 million which is being amortised over the life of the
patent. The patent cost $11,600. In September 2006 a competitor announced the successful completion of
preliminary trials on an alternative drug with the same beneficial properties as Tournose. The alternative drug is
expected to be readily available in two years time. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Seymour Co for the year ended
30 September 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案: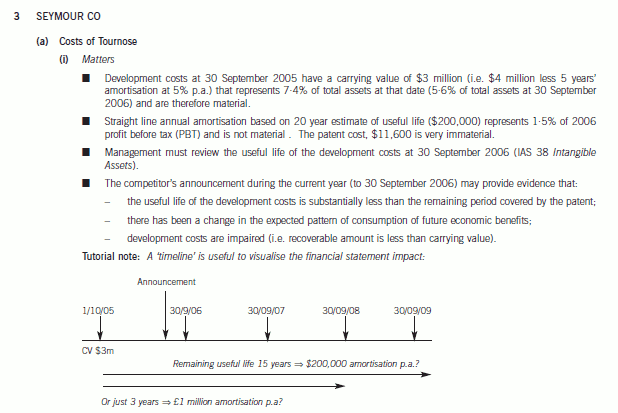
■ A change in the estimated useful life should be accounted for as a change in accounting estimate in accordance
with IAS 8 Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors. For example, if the development
costs have little, if any, useful life after the introduction of the alternative drug (‘worst case’ scenario), the carrying
value ($3 million) should be written off over the current and remaining years, i.e. $1 million p.a. The increase in
amortisation/decrease in carrying value ($800,000) is material to PBT (6%) and total assets (1·5%).
■ Similarly a change in the expected pattern of consumption of the future economic benefits should be accounted for
as a change in accounting estimate (IAS 8). For example, it may be that the useful life is still to 2020 but that
the economic benefits may reduce significantly in two years time.
■ After adjusting the carrying amount to take account of the change in accounting estimate(s) management should
have tested it for impairment and any impairment loss recognised in profit or loss.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ $3 million carrying amount of development costs brought forward agreed to prior year working papers and financial
statements.
■ A copy of the press release announcing the competitor’s alternative drug.
■ Management’s projections of future cashflows from Tournose-related sales as evidence of the useful life of the
development costs and pattern of consumption.
■ Reperformance of management’s impairment test on the development costs: Recalculation of management’s
calculation of the carrying amount after revising estimates of useful life and/or consumption of benefits compared
with management’s calculation of value in use.
■ Sensitivity analysis on management’s key assumptions (e.g. estimates of useful life, discount rate).
■ Written management representation on the key assumptions concerning the future that have a significant risk of
causing material adjustment to the carrying amount of the development costs. (These assumptions should be
disclosed in accordance with IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements.) -
第17题:
(b) You are an audit manager in a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants currently assigned to the audit of Cleeves
Co for the year ended 30 September 2006. During the year Cleeves acquired a 100% interest in Howard Co.
Howard is material to Cleeves and audited by another firm, Parr & Co. You have just received Parr’s draft
auditor’s report for the year ended 30 September 2006. The wording is that of an unmodified report except for
the opinion paragraph which is as follows:
Audit opinion
As more fully explained in notes 11 and 15 impairment losses on non-current assets have not been
recognised in profit or loss as the directors are unable to quantify the amounts.
In our opinion, provision should be made for these as required by International Accounting Standard 36
(Impairment). If the provision had been so recognised the effect would have been to increase the loss before
and after tax for the year and to reduce the value of tangible and intangible non-current assets. However,
as the directors are unable to quantify the amounts we are unable to indicate the financial effect of such
omissions.
In view of the failure to provide for the impairments referred to above, in our opinion the financial statements
do not present fairly in all material respects the financial position of Howard Co as of 30 September 2006
and of its loss and its cash flows for the year then ended in accordance with International Financial Reporting
Standards.
Your review of the prior year auditor’s report shows that the 2005 audit opinion was worded identically.
Required:
(i) Critically appraise the appropriateness of the audit opinion given by Parr & Co on the financial
statements of Howard Co, for the years ended 30 September 2006 and 2005. (7 marks)
正确答案:(b) (i) Appropriateness of audit opinion given
Tutorial note: The answer points suggested by the marking scheme are listed in roughly the order in which they might
be extracted from the information presented in the question. The suggested answer groups together some of these
points under headings to give the analysis of the situation a possible structure.
Heading
■ The opinion paragraph is not properly headed. It does not state the form. of the opinion that has been given nor
the grounds for qualification.
■ The opinion ‘the financial statements do not give a true and fair view’ is an ‘adverse’ opinion.
■ That ‘provision should be made’, but has not, is a matter of disagreement that should be clearly stated as noncompliance
with IAS 36. The title of IAS 36 Impairment of Assets should be given in full.
■ The opinion should be headed ‘Disagreement on Accounting Policies – Inappropriate Accounting Method – Adverse
Opinion’.
1 ISA 250 does not specify with whom agreement should be reached but presumably with those charged with corporate governance (e.g audit committee or
2 other supervisory board).
20
6D–INTBA
Paper 3.1INT
Content
■ It is appropriate that the opinion paragraph should refer to the note(s) in the financial statements where the matter
giving rise to the modification is more fully explained. However, this is not an excuse for the audit opinion being
‘light’ on detail. For example, the reason for impairment could be summarised in the auditor’s report.
■ The effects have not been quantified, but they should be quantifiable. The maximum possible loss would be the
carrying amount of the non-current assets identified as impaired.
■ It is not clear why the directors have been ‘unable to quantify the amounts’. Since impairments should be
quantifiable any ‘inability’ suggest a limitation in scope of the audit, in which case the opinion should be disclaimed
(or ‘except for’) on grounds of lack of evidence rather than disagreement.
■ The wording is confusing. ‘Failure to provide’ suggests disagreement. However, there must be sufficient evidence
to support any disagreement. Although the directors cannot quantify the amounts it seems the auditors must have
been able to (estimate at least) in order to form. an opinion that the amounts involved are sufficiently material to
warrant a qualification.
■ The first paragraph refers to ‘non-current assets’. The second paragraph specifies ‘tangible and intangible assets’.
There is no explanation why or how both tangible and intangible assets are impaired.
■ The first paragraph refers to ‘profit or loss’ and the second and third paragraphs to ‘loss’. It may be clearer if the
first paragraph were to refer to recognition in the income statement.
■ It is not clear why the failure to recognise impairment warrants an adverse opinion rather than ‘except for’. The
effects of non-compliance with IAS 36 are to overstate the carrying amount(s) of non-current assets (that can be
specified) and to understate the loss. The matter does not appear to be pervasive and so an adverse opinion looks
unsuitable as the financial statements as a whole are not incomplete or misleading. A loss is already being reported
so it is not that a reported profit would be turned into a loss (which is sometimes judged to be ‘pervasive’).
Prior year
■ As the 2005 auditor’s report, as previously issued, included an adverse opinion and the matter that gave rise to
the modification:
– is unresolved; and
– results in a modification of the 2006 auditor’s report,
the 2006 auditor’s report should also be modified regarding the corresponding figures (ISA 710 Comparatives).
■ The 2006 auditor’s report does not refer to the prior period modification nor highlight that the matter resulting in
the current period modification is not new. For example, the report could say ‘As previously reported and as more
fully explained in notes ….’ and state ‘increase the loss by $x (2005 – $y)’. -
第18题:
The following trial balance relates to Sandown at 30 September 2009:
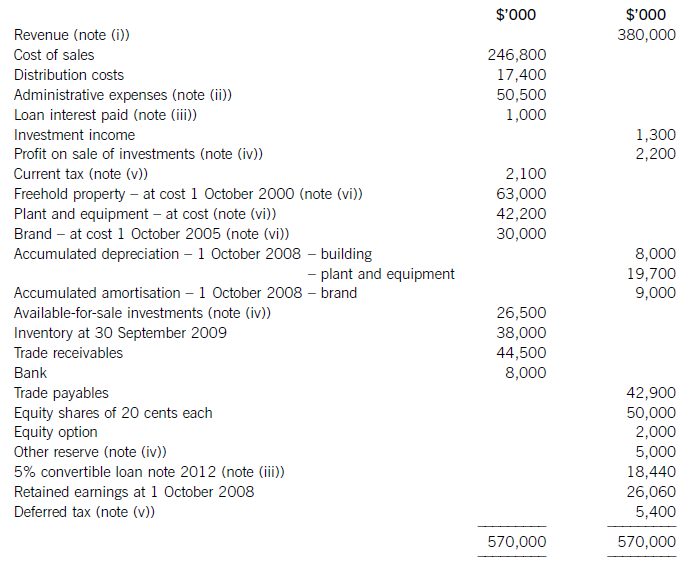
The following notes are relevant:
(i) Sandown’s revenue includes $16 million for goods sold to Pending on 1 October 2008. The terms of the sale are that Sandown will incur ongoing service and support costs of $1·2 million per annum for three years after the sale. Sandown normally makes a gross profit of 40% on such servicing and support work. Ignore the time value of money.
(ii) Administrative expenses include an equity dividend of 4·8 cents per share paid during the year.
(iii) The 5% convertible loan note was issued for proceeds of $20 million on 1 October 2007. It has an effective interest rate of 8% due to the value of its conversion option.
(iv) During the year Sandown sold an available-for-sale investment for $11 million. At the date of sale it had a
carrying amount of $8·8 million and had originally cost $7 million. Sandown has recorded the disposal of the
investment. The remaining available-for-sale investments (the $26·5 million in the trial balance) have a fair value of $29 million at 30 September 2009. The other reserve in the trial balance represents the net increase in the value of the available-for-sale investments as at 1 October 2008. Ignore deferred tax on these transactions.
(v) The balance on current tax represents the under/over provision of the tax liability for the year ended 30 September 2008. The directors have estimated the provision for income tax for the year ended 30 September 2009 at $16·2 million. At 30 September 2009 the carrying amounts of Sandown’s net assets were $13 million in excess of their tax base. The income tax rate of Sandown is 30%.
(vi) Non-current assets:
The freehold property has a land element of $13 million. The building element is being depreciated on a
straight-line basis.
Plant and equipment is depreciated at 40% per annum using the reducing balance method.
Sandown’s brand in the trial balance relates to a product line that received bad publicity during the year which led to falling sales revenues. An impairment review was conducted on 1 April 2009 which concluded that, based on estimated future sales, the brand had a value in use of $12 million and a remaining life of only three years.
However, on the same date as the impairment review, Sandown received an offer to purchase the brand for
$15 million. Prior to the impairment review, it was being depreciated using the straight-line method over a
10-year life.
No depreciation/amortisation has yet been charged on any non-current asset for the year ended 30 September
2009. Depreciation, amortisation and impairment charges are all charged to cost of sales.
Required:
(a) Prepare the statement of comprehensive income for Sandown for the year ended 30 September 2009.
(13 marks)
(b) Prepare the statement of financial position of Sandown as at 30 September 2009. (12 marks)
Notes to the financial statements are not required.
A statement of changes in equity is not required.
正确答案:
(i)IAS18Revenuerequiresthatwheresalesrevenueincludesanamountforaftersalesservicingandsupportcoststhenaproportionoftherevenueshouldbedeferred.Theamountdeferredshouldcoverthecostandareasonableprofit(inthiscaseagrossprofitof40%)ontheservices.Astheservicingandsupportisforthreeyearsandthedateofthesalewas1October2008,revenuerelatingtotwoyears’servicingandsupportprovisionmustbedeferred:($1·2millionx2/0·6)=$4million.Thisisshownas$2millioninbothcurrentandnon-currentliabilities. -
第19题:
(a) The following figures have been calculated from the financial statements (including comparatives) of Barstead for
the year ended 30 September 2009:
increase in profit after taxation 80%
increase in (basic) earnings per share 5%
increase in diluted earnings per share 2%
Required:
Explain why the three measures of earnings (profit) growth for the same company over the same period can
give apparently differing impressions. (4 marks)
(b) The profit after tax for Barstead for the year ended 30 September 2009 was $15 million. At 1 October 2008 the company had in issue 36 million equity shares and a $10 million 8% convertible loan note. The loan note will mature in 2010 and will be redeemed at par or converted to equity shares on the basis of 25 shares for each $100 of loan note at the loan-note holders’ option. On 1 January 2009 Barstead made a fully subscribed rights issue of one new share for every four shares held at a price of $2·80 each. The market price of the equity shares of Barstead immediately before the issue was $3·80. The earnings per share (EPS) reported for the year ended 30 September 2008 was 35 cents.
Barstead’s income tax rate is 25%.
Required:
Calculate the (basic) EPS figure for Barstead (including comparatives) and the diluted EPS (comparatives not required) that would be disclosed for the year ended 30 September 2009. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(a)Whilstprofitaftertax(anditsgrowth)isausefulmeasure,itmaynotgiveafairrepresentationofthetrueunderlyingearningsperformance.Inthisexample,userscouldinterpretthelargeannualincreaseinprofitaftertaxof80%asbeingindicativeofanunderlyingimprovementinprofitability(ratherthanwhatitreallyis:anincreaseinabsoluteprofit).Itispossible,evenprobable,that(someof)theprofitgrowthhasbeenachievedthroughtheacquisitionofothercompanies(acquisitivegrowth).Wherecompaniesareacquiredfromtheproceedsofanewissueofshares,orwheretheyhavebeenacquiredthroughshareexchanges,thiswillresultinagreaternumberofequitysharesoftheacquiringcompanybeinginissue.ThisiswhatappearstohavehappenedinthecaseofBarsteadastheimprovementindicatedbyitsearningspershare(EPS)isonly5%perannum.ThisexplainswhytheEPS(andthetrendofEPS)isconsideredamorereliableindicatorofperformancebecausetheadditionalprofitswhichcouldbeexpectedfromthegreaterresources(proceedsfromthesharesissued)ismatchedwiththeincreaseinthenumberofshares.Simplylookingatthegrowthinacompany’sprofitaftertaxdoesnottakeintoaccountanyincreasesintheresourcesusedtoearnthem.Anyincreaseingrowthfinancedbyborrowings(debt)wouldnothavethesameimpactonprofit(asbeingfinancedbyequityshares)becausethefinancecostsofthedebtwouldacttoreduceprofit.ThecalculationofadilutedEPStakesintoaccountanypotentialequitysharesinissue.Potentialordinarysharesarisefromfinancialinstruments(e.g.convertibleloannotesandoptions)thatmayentitletheirholderstoequitysharesinthefuture.ThedilutedEPSisusefulasitalertsexistingshareholderstothefactthatfutureEPSmaybereducedasaresultofsharecapitalchanges;inasenseitisawarningsign.InthiscasethelowerincreaseinthedilutedEPSisevidencethatthe(higher)increaseinthebasicEPShas,inpart,beenachievedthroughtheincreaseduseofdilutingfinancialinstruments.Thefinancecostoftheseinstrumentsislessthantheearningstheirproceedshavegeneratedleadingtoanincreaseincurrentprofits(andbasicEPS);however,inthefuturetheywillcausemoresharestobeissued.ThiscausesadilutionwherethefinancecostperpotentialnewshareislessthanthebasicEPS. -
第20题:
Under certain circumstances, profits made on transactions between members of a group need to be eliminated from the consolidated financial statements under IFRS.
Which of the following statements about intra-group profits in consolidated financial statements is/are correct?
(i) The profit made by a parent on the sale of goods to a subsidiary is only realised when the subsidiary sells the goods to a third party
(ii) Eliminating intra-group unrealised profits never affects non-controlling interests
(iii) The profit element of goods supplied by the parent to an associate and held in year-end inventory must be eliminated in full
A.(i) only
B.(i) and (ii)
C.(ii) and (iii)
D.(iii) only
正确答案:A(i) is the only correct elimination required by IFRS.
-
第21题:
Which of the following commands should be used to obtain information about the software packages available on the installation media?()
- A、 lsattr
- B、 inutoc
- C、 installp
- D、 lsresource
正确答案:C -
第22题:
单选题Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding automatic identification systems(AIS)().AAIS is a global tracking system that relies upon INMARSAT C service to communicate vessel position and other safety related information to similarly equipped vessels,aircraft and shore stations within the area
BAIS is a short-range 3 cm X-band radar system that automatically sends a vessel's position and other safety related information to similarly equipped vessels,aircraft and shore stations within the area
CAIS is a short-range VHF-FM system that automatically broadcasts a vessel's position and other safety related information frequently to similarly equipped vessels,aircraft and shore stations within the area
DAIS is a one-way centrally managed system that requires the local VTS to send commands to instruct each vessel to broadcast position and other safety related information to similarly equipped vessels,aircraft and shore stations within the area
正确答案: D解析: 暂无解析 -
第23题:
单选题According to the speaker, as an investor you should do the following EXCEPT ______.Aresearching financial pages of the Wall Street Journal
Bkeeping an eye on the stock market
Cconsulting an expert on investment
Dsearching for as much information as possible about the listed companies
正确答案: C解析:
事实细节的找寻和判断。该段录音开头便点明主题,指出投资者要做两件重要的事情:调查和研究。接着对投资者具体应如何做进行了详细说明,提到了选项A,B和D的内容。只有选项C(向投资专家咨询)未曾提及。
【录音原文】
There are two very important things you must do as an investor—before any of your hard-earned money leaves your hand—and that is to research and to study. You must research the financial pages of your local newspaper as well as the Wall Street Journal, and any other publications you can get your hands on. Decide which stocks are affordable, are performing well, and have a good track record. Visit your local library and study all the information you can find on the stocks you are considering buying into. Find out what plans for expansion the companies have. Study the market and find out as much valuable information as you can about each company.
